Assessment of the Biocontrol Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Trichoderma asperellum Against Infected Hordeum vulgare L. Germination
- PMID: 39768268
- PMCID: PMC11676777
- DOI: 10.3390/life14121560
Assessment of the Biocontrol Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Trichoderma asperellum Against Infected Hordeum vulgare L. Germination
Abstract
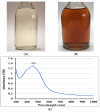
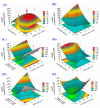
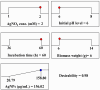
This study investigated the biosynthesis, statistical optimization, characterization, and biocontrol activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) produced by newly isolated Trichoderma sp. The Trichoderma asperellum strain TA-3N was identified based on the ITS gene sequence, together with its phenotypic characteristics (GenBank accession number: OM321439). The color change from light yellow to brown after the incubation period indicates AgNPs biosynthesis. The UV spectrum revealed a single peak with the maximum absorption at 453 nm, indicating that T. asperellum produces AgNPs effectively. A Rotatable Central Composite Design (RCCD) was used to optimize the biosynthesis of AgNPs using the aqueous mycelial-free filtrate of T. asperellum. The optimal conditions for maximum AgNPs biosynthesis (156.02 µg/mL) were predicted theoretically using the desirability function tool and verified experimentally. The highest biosynthetic produced AgNPs by T. asperellum reached 160.3 µg/mL using AgNO3 concentration of 2 mM/mL, initial pH level of 6, incubation time of 60 h, and biomass weight of 6 g/100 mL water. SEM and TEM imaging revealed uniform spherical shape particles that varied in size between 8.17 and 17.74 nm. The synthesized AgNPs have a Zeta potential value of -9.51 mV. FTIR analysis provided insights into the surface composition of AgNPs, identifying various functional groups such as N-H, -OH, C-H, C=O, and the amide I bond in proteins. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity assays demonstrated that AgNPs in combination with T. asperellum can mitigate the toxic effects of Fusarium oxysporum on barley. This intervention markedly enhanced cell division rates and decreased chromosomal irregularities. The results indicate that AgNPs synthesized by T. asperellum show the potential as an eco-friendly and efficient method for controlling plant diseases. Further studies are necessary to investigate their possible use in the agricultural sector.
Keywords: Trichoderma asperellum; barley; biocontrol activity; biosynthesis; characterization; cyto-genotoxicity assay; silver nanoparticles; statistical optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Aziz Z.A.A., Mohd-Nasir H., Ahmad A., Setapar S.H.M., Peng W.L., Chuo S.C., Khatoon A., Umar K., Yaqoob A.A., Mohamad Ibrahim M.N. Role of nanotechnology for design and development of cosmeceutical: Application in makeup and skin care. Front. Chem. 2019;7:739. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00739. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rana A., Yadav K., Jagadevan S. A comprehensive review on green synthesis of nature-inspired metal nanoparticles: Mechanism, application and toxicity. J. Clean. Prod. 2020;272:122880. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122880. - DOI
-
- Srinivasan L.V., Rana S.S. A critical review of various synthesis methods of nanoparticles and their applications in biomedical, regenerative medicine, food packaging, and environment. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024;6:371. doi: 10.1007/s42452-024-06040-8. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

