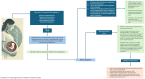
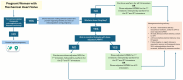
Role of Antiplatelets and Anticoagulation Therapies in Pregnancy
- PMID: 39768679
- PMCID: PMC11678094
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13247757
Role of Antiplatelets and Anticoagulation Therapies in Pregnancy
Abstract
Thrombosis is an important cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Pregnancy is a hypercoagulable state, and thrombotic complications in pregnancy are a major cause of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Current guidelines support the selective use of aspirin, heparin, and warfarin in pregnant women. The decision to treat with antiplatelets and anticoagulants during pregnancy can be challenging, as these agents have numerous indications and contraindications, potential teratogenicity, and dosing considerations. Their use requires thoughtful discussion between patient and provider that balances therapeutic benefit versus maternal and fetal risks, while accounting for a safe delivery plan. Our aim is to provide a narrative review of the established and emerging indications of antiplatelets and anticoagulants, discuss their appropriate timing of administration, and consider their associated adverse fetal and maternal risks.
Keywords: anticoagulation; antiplatelets; congenital heart disease; hypercoagulable disorders; mechanical valve; preeclampsia; pregnancy; thrombophilia; thrombosis; valvular heart disease; venous thromboembolism; vitamin K antagonist.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources