Pharmacological Strategies to Decrease Long-Term Prescription Opioid Use: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39768692
- PMCID: PMC11728354
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13247770
Pharmacological Strategies to Decrease Long-Term Prescription Opioid Use: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background/Objectives: As long-term prescription opioid use is associated with increased morbidity and mortality, timely dose reduction of prescription opioids should be considered. However, most research has been conducted on patients using heroin. Given the differences between prescription and illicit opioid use, the aim of this review was to provide an overview of pharmacological strategies to reduce prescription opioid use or improve clinical outcomes for people who experience long-term prescription opioid use, including those with opioid use disorder. Methods: We conducted a systematic database search of PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, and the Cochrane Library. Outcomes included dose reduction, treatment dropout, pain, addiction, and outcomes relating to quality of life (depression, functioning, quality of life). Results: We identified thirteen studies (eight randomized controlled trials and five observational studies). Pharmacological strategies were categorized into two categories: (1) deprescribing (tapering) opioids or (2) opioid agonist treatment (OAT) with long-acting opioids. Tapering strategies decreased opioid dosage and had mixed effects on pain and addiction. OAT with buprenorphine or methadone led to improvements in pain relief and quality of life, with a slight (non-significant) preference for methadone in terms of treatment retention (RR = 1.10 [CI: 0.89-1.37]) but not for other outcomes. Most studies had high dropout rates and a serious risk of bias. Conclusions: Tapering reduced prescription opioid doses had mixed effects on pain. OAT improved clinical outcomes without dose reduction. Based on our review findings, there is no clear preference for either tapering or OAT. Tapering may be considered first as it reduces dependency, tolerance, and side effects, but is associated with adverse events and not always feasible. OAT can be a suitable alternative. Non-pharmacological interventions may facilitate tapering. Further research is needed to identify novel pharmacological strategies to facilitate opioid tapering. Registration: PROSPERO 2022 CRD42022323468.
Keywords: opioid agonist treatment; opioid rotation; opioid tapering; prescription opioid misuse; prescription opioid use disorder; prescription opioids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
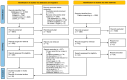
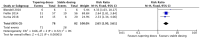
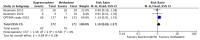
References
-
- Nury E., Schmucker C., Nagavci B., Motschall E., Nitschke K., Schulte E., Wegwarth O., Meerpohl J.J. Efficacy and safety of strong opioids for chronic non-cancer pain and chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analyses. PAIN. 2021;163:610–636. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002423. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leung J., Santo T., Colledge-Frisby S., Mekonen T., Thomson K., Degenhardt L., Connor J.P., Hall W., Stjepanović D. Mood and anxiety symptoms in persons taking prescription opioids: A systematic review with meta-analyses of longitudinal studies. Pain Med. 2022;23:1442–1456. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnac029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

