Potential Serum HMGB1, HSP90, and S100A9 as Metastasis Predictive Biomarkers for Cancer Patients and Relevant Cytokines: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 39768997
- PMCID: PMC11675498
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413232
Potential Serum HMGB1, HSP90, and S100A9 as Metastasis Predictive Biomarkers for Cancer Patients and Relevant Cytokines: A Pilot Study
Abstract
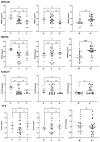
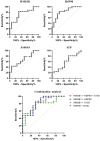
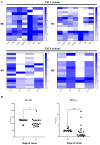
Metastatic cancer is still one of the leading causes of death worldwide despite significant advancements in diagnosis and treatment. Biomarkers are one of the most promising diagnostic tools that are used alongside traditional diagnostic tools in cancer patients. DAMPs are intracellular molecules released in response to cellular stress, tissue injury, and cell death. There have been shown to be associated with worsening prognosis among such patients, and some DAMPs could potentially be used as predictive biomarkers of metastatic status. The goal of this study is to investigate DAMP expression and the probability that certain DAMPs could be predictive biomarkers of the metastatic stage in various cancer types. Forty cancer patients at Naresuan University Hospital, Thailand, were enrolled. Then, an investigation of HSP90, HMGB1, S100A9, and ATP expression and cytokine/chemokine profiling in serum was performed using an immunological-based assay. We assessed the predictive biomarker candidates and the association between DAMP expression and cytokines/chemokines using an ROC curve analysis and a correlation regression analysis. The results showed that HSP90 has strong potential as a metastatic predictive biomarker, with a cutoff value of 25.46 ng/mL (AUC 0.8207, sensitivity 82.61%, specificity 75.00%, 95% CI 0.6860-0.9553). This was followed by HMGB1 and S100A9, which exhibited sensitivity of 82.61 and 65.22%, and specificity of 68.75 and 56.25%, respectively. Interestingly, the candidate DAMPs negatively correlate with various serum cytokines, for example, HMGB1 vs. IL-15 (slope 88.05, R 0.3297, p-value 0.005), HMGB1 vs. IFN-γ (slope 2.235, R 0.3052, p-value 0.0013) and HSP90 vs. IFN-γ (slope 0.0614, R 0.2187, p-value 0.008), suggesting that they are highly elevated in advanced metastatic tumors, which is possibly associated with the immunomodulation effect. We postulated that HSP90, HMGB1, and S100A9 have the potential to be predictive biomarkers for supporting tumor metastasis categorization using histopathology.
Keywords: DAMPs; HMGB1; HSP90; S100A9; TNM staging; cancer chemokines; cancer cytokines; metastasis predictive biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

