Metal-Dependent Cell Death in Renal Fibrosis: Now and in the Future
- PMID: 39769044
- PMCID: PMC11678559
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413279
Metal-Dependent Cell Death in Renal Fibrosis: Now and in the Future
Abstract
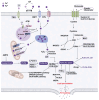
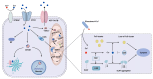
Renal fibrosis is a common final pathway underlying nearly almost all progressive kidney diseases. Metal ions are essential trace elements in organisms and are involved in important physiological activities. However, aberrations in intracellular metal ion metabolism may disrupt homeostasis, causing cell death and increasing susceptibility to various diseases. Accumulating evidence suggests a complex association between metal-dependent cell death and renal fibrosis. In this article, we provide a comprehensive overview of the specific molecular mechanisms of metal-dependent cell death and their crosstalk, up-to-date evidence supporting their role in renal fibrosis, therapeutic targeting strategies, and research needs, aiming to offer a rationale for future clinical treatment of renal fibrosis.
Keywords: cell death; cuproptosis; ferroptosis; metal ions; renal fibrosis; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

