Audiological Features in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39769062
- PMCID: PMC11676466
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413290
Audiological Features in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
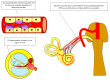
Hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis has been underestimated for decades. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect both the middle ear (specifically, the incudomalleolar and incudostapedial joints) and inner ear (including the cochlea and acoustic nerve) simultaneously. Despite ongoing research, consensus on effective treatments for hearing impairment in these patients remains elusive. This systematic review aims to consolidate clinically relevant information for healthcare providers by summarizing current evidence on hearing impairment in rheumatoid arthritis patients. We conducted the current systematic review by searching platforms of PubMed, Embase, ClinicalKey, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect to retrieve eligible articles regarding hearing impairment related to rheumatoid arthritis. We extract any data on characteristics, pathophysiology, examination, and treatment related to rheumatoid arthritis. Based on the currently available evidence, we advocate for the use of specific audiometric tests to facilitate early detection of hearing impairment in these patients. Regular audiological assessments are recommended to monitor hearing ability and potentially prevent further deterioration. Finally, we propose a modified treatment protocol that integrates steroids, hydroxychloroquine, and non-invasive brain stimulation as a novel therapeutic approach for managing these symptoms. This protocol aims to offer clinicians new strategies to address hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis effectively.
Keywords: cochleopathy; hearing impairment; neuropathy; ossicles; rheumatoid arthritis; steroid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there were no potential conflict of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Grommets (ventilation tubes) for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jan 25;(1):CD001801. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001801.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Oct 06;(10):CD001801. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001801.pub3. PMID: 15674886 Updated.
-
Bilateral versus unilateral hearing aids for bilateral hearing impairment in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 19;12(12):CD012665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012665.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29256573 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Platinum-induced hearing loss after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 3;2016(8):CD010181. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010181.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27486906 Free PMC article.
-
Topical antibiotics with steroids for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013054.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484406
Cited by
-
Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Patients with Hashimoto's Disease: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 14;26(10):4703. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104703. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk of Hearing Loss in Patients Treated with Exendin-4 Derivatives: A Network Meta-Analysis of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 16;18(5):735. doi: 10.3390/ph18050735. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dikici O., Muluk N.B., Tosun A.K., Unlusoy I. Subjective audiological tests and transient evoked otoacoustic emissions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Analysis of the factors affecting hearing levels. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266:1719–1726. doi: 10.1007/s00405-009-0975-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takatsu M., Higaki M., Kinoshita H., Mizushima Y., Koizuka I. Ear involvement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Otol. Neurotol. 2005;26:755–761. doi: 10.1097/01.mao.0000178138.19848.bd. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

