Nanoparticle Strategies for Treating CNS Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Drug Delivery and Theranostic Applications
- PMID: 39769066
- PMCID: PMC11676454
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413302
Nanoparticle Strategies for Treating CNS Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Drug Delivery and Theranostic Applications
Abstract
This review aims to address the significant challenges of treating central nervous system (CNS) disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases, strokes, spinal cord injuries, and brain tumors. These disorders are difficult to manage due to the complexity of disease mechanisms and the protective blood-brain barrier (BBB), which restricts drug delivery. Recent advancements in nanoparticle (NP) technologies offer promising solutions, with potential applications in drug delivery, neuroprotection, and neuroregeneration. By examining current research, we explore how NPs can cross the BBB, deliver medications directly to targeted CNS regions, and enhance both diagnostics and treatment. Key NP strategies, such as passive targeting, receptor-mediated transport, and stimuli-responsive systems, demonstrate encouraging results. Studies show that NPs may improve drug delivery, minimize side effects, and increase therapeutic effectiveness in models of Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, stroke, and glioblastoma. NP technologies thus represent a promising approach for CNS disorder management, combining drug delivery and diagnostic capabilities to enable more precise and effective treatments that could significantly benefit patient outcomes.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; blood–brain barrier; nanomedicine; nanoparticles; nanotechnology; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroregeneration; targeted drug delivery; theranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
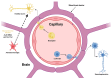
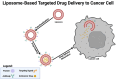
References
-
- Yadav V.K., Choudhary N., Gacem A., Verma R.K., Abul Hasan M., Tarique Imam M., Almalki Z.S., Yadav K.K., Park H.-K., Ghosh T., et al. Deeper insight into ferroptosis: Association with Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, and brain tumors and their possible treatment by nanomaterials induced ferroptosis. Redox Rep. 2023;28:2269331. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2023.2269331. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

