The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Remodeling
- PMID: 39769102
- PMCID: PMC11728060
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413335
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Remodeling
Abstract
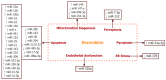
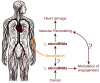
Doxorubicin (DOX), a cornerstone chemotherapeutic agent, effectively combats various malignancies but is marred by significant cardiovascular toxicity, including endothelial damage, chronic heart failure, and vascular remodeling. These adverse effects, mediated by oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammatory pathways, and dysregulated autophagy, underscore the need for precise therapeutic strategies. Emerging research highlights the critical role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in DOX-induced vascular remodeling and cardiotoxicity. miRNAs, such as miR-21, miR-22, miR-25, miR-126, miR-140-5p, miR-330-5p, miR-146, miR-143, miR-375, miR-125b, miR-451, miR-34a-5p, and miR-9, influence signaling pathways like TGF-β/Smad, AMPKa/SIRT, NF-κB, mTOR, VEGF, and PI3K/AKT/Nrf2, impacting vascular homeostasis, angiogenesis, and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Despite existing studies, gaps remain in understanding the full spectrum of miRNAs involved and their downstream effects on vascular remodeling. This review synthesizes the current knowledge on miRNA dysregulation during DOX exposure, focusing on their dual roles in cardiovascular pathology and tumor progression. Strategies to reduce DOX cardiotoxicity include modulating miRNA expression to restore signaling balance, targeting pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic pathways, and leveraging miRNA inhibitors or mimics. This review aims to organize and integrate the existing knowledge on the role of miRNAs in vascular remodeling, particularly in the contexts of DOX treatment and the progression of various cardiovascular diseases, including their potential involvement in tumor growth.
Keywords: biomarker; doxorubicin; endothelium; heart disease; microRNA; tumor angiogenesis; vascular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines: 22nd List. 2021. [(accessed on 30 September 2021)]. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/325771.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

