Gene Variant Related Neurological and Molecular Biomarkers Predict Psychosis Progression, with Potential for Monitoring and Prevention
- PMID: 39769114
- PMCID: PMC11677369
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413348
Gene Variant Related Neurological and Molecular Biomarkers Predict Psychosis Progression, with Potential for Monitoring and Prevention
Abstract
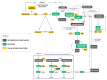
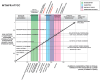
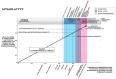
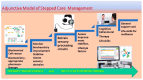
The (MTHFR) C677T gene polymorphism is associated with neurological disorders and schizophrenia. Patients diagnosed with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder and controls (n 134) had data collected for risk factors, molecular and neuro-sensory variables, symptoms, and functional outcomes. Promising gene variant-related predictive biomarkers were identified for diagnosis by Receiver Operating Characteristics and for illness duration by linear regression. These were then analyzed using Spearman's correlation in relation to the duration of illness. Significant correlations were ranked by strength and plotted on graphs for each MTHFR C677T variant. Homozygous MTHFR 677 TT carriers displayed a mid-illness switch to depression, with suicidality and a late-phase shift from lower to higher methylation, with activated psychosis symptoms. MTHFR 677 CC variant carriers displayed significant premorbid correlates for family history, developmental disorder, learning disorder, and head injury. These findings align with those of low methylation, oxidative stress, multiple neuro-sensory processing deficits, and disability outcomes. Heterozygous MTHFR 677 CT carriers displayed multiple shifts in mood and methylation with multiple adverse outcomes. The graphically presented ranked biomarker correlates for illness duration allow a perspective of psychosis development across gene variants, with the potential for phase of illness monitoring and new therapeutic insights to prevent or delay psychosis and its adverse outcomes.
Keywords: MTHFR C677T; bipolar; disease progression; hostility; methylation; prognosis; risk prediction; schizophrenia; sensory processing; suicide; treatment resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Stephanie Fryar-Williams is a Director of Youth in Mind Research Institute Pty Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. A patent application was filed in September 2017 (PCT/AU2017/051049).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanism Biomarkers Predict Diagnosis in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis, with Implications for Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15845. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115845. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958826 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific effects of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms on schizophrenia with methylation changes.Compr Psychiatry. 2019 Oct;94:152121. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2019.152121. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Compr Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31476590
-
Molecular Mechanisms Provide a Landscape for Biomarker Selection for Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15296. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015296. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism with primary glaucoma in Saudi population.BMC Ophthalmol. 2016 Sep 1;16(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12886-016-0337-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27585654 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of MTHFR gene variants in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and unipolar depressive disorder: evidence for a common genetic vulnerability?Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Nov;25(8):1530-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.12.006. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 21185933 Review.
References
-
- Dimulescu C., Gareayaghi S., Kamp F., Fromm S., Obermayer K., Metzner C. Structural Differences Between Healthy Subjects and Patients With Schizophrenia or Schizoaffective Disorder: A Graph and Control Theoretical Perspective. Front. Psychiatry. 2021;12:669783. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.669783. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

