Innovative Biotherapies and Nanotechnology in Osteoarthritis: Advancements in Inflammation Control and Cartilage Regeneration
- PMID: 39769149
- PMCID: PMC11677281
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413384
Innovative Biotherapies and Nanotechnology in Osteoarthritis: Advancements in Inflammation Control and Cartilage Regeneration
Abstract
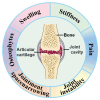
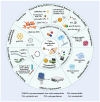
Osteoarthritis (OA) is among the most prevalent degenerative joint disorders worldwide, particularly affecting the aging population and imposing significant disability and economic burdens. The disease is characterized by progressive degradation of articular cartilage and chronic inflammation, with no effective long-term treatments currently available to address the underlying causes of its progression. Conventional therapies primarily manage symptoms such as pain and inflammation but fail to repair damaged tissues. Emerging biotherapies and regenerative medicine approaches offer promising alternatives by addressing cartilage repair and inflammation control at the molecular level. This review explores the recent advancements in biotherapeutic strategies, including mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy, growth factors, and tissue engineering, which hold the potential for promoting cartilage regeneration and modulating the inflammatory microenvironment. Additionally, the integration of nanotechnology has opened new avenues for targeted drug delivery systems and the development of innovative nanomaterials that can further enhance the efficacy of biotherapies by precisely targeting inflammation and cartilage damage. This article concludes by discussing the current clinical applications, the ongoing clinical trials, and the future research directions necessary to confirm the safety and efficacy of these advanced therapies for OA management. With these advancements, biotherapies combined with nanotechnology may revolutionize the future of OA treatment by offering precise and effective solutions for long-term disease management and improved patient outcomes.
Keywords: biotherapies; cartilage repair; inflammation; nanotechnology; osteoarthritis; regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional Biomolecule Delivery Systems and Bioengineering in Cartilage Regeneration.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20(1):32-46. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666190206202048. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30727886 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of articular cartilage degeneration: New biological insights for an old-timer cell.Cytotherapy. 2019 Dec;21(12):1179-1197. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Cytotherapy. 2019. PMID: 31784241 Review.
-
Emerging Strategies in Cartilage Repair and Joint Preservation.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Dec 27;61(1):24. doi: 10.3390/medicina61010024. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39859006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Strategies for Cartilage Regeneration in Osteoarthritis.Tissue Eng Part A. 2024 Apr;30(7-8):259-271. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2023.0255. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Tissue Eng Part A. 2024. PMID: 38126327 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells in connective tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: applications in cartilage repair and osteoarthritis therapy.Histol Histopathol. 2009 Mar;24(3):347-66. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.347. Histol Histopathol. 2009. PMID: 19130405 Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of MSCs, iPSCs, and EVs in the Repair of Human MSK Tissues: Is Ultimate Success Dependent on Developing Excellent Implant Materials as Well as Creating an Optimal Environment for Implantation? What Is the Rationale for These Choices?Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 28;26(13):6250. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136250. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion Currents Mediated by TRPA1 Channels in Freshly Dissociated Rat Articular Chondrocytes: Biophysical Properties and Regulation by Inflammatory Processes.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;18(3):332. doi: 10.3390/ph18030332. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cross M., Smith E., Hoy D., Nolte S., Ackerman I., Fransen M., Bridgett L., Williams S., Guillemin F., Hill C.L., et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: Estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014;73:1323–1330. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204763. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hunter D.J., Schofield D., Callander E. The individual and socioeconomic impact of osteoarthritis, Nature reviews. Rheumatology. 2014;10:437–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

