Nigella sativa: A Comprehensive Review of Its Therapeutic Potential, Pharmacological Properties, and Clinical Applications
- PMID: 39769174
- PMCID: PMC11677364
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413410
Nigella sativa: A Comprehensive Review of Its Therapeutic Potential, Pharmacological Properties, and Clinical Applications
Abstract
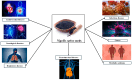
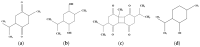
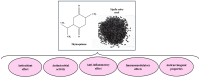
Nigella sativa (NS) is an annual herb belonging to the Ranunculaceae family, also known as black cumin or black seed. This plant has been used since ancient times due to its therapeutic properties and has proven effective in gastrointestinal, respiratory, cardiovascular, infectious, and inflammatory conditions. In this review, the aim is to highlight the therapeutic effects of the plant known in Arab countries as "the plant that cures any disease", which are provided by the phytochemical compounds in its composition, such as thymoquinone, p-cymene, α-thujene, longifolene, β-pinene, α-pinene, and carvacrol. These compounds confer an antioxidant effect to the seeds, leading to a significant decrease in ROS and a potent anti-inflammatory effect. Also, in this review, the aim is to highlight that NS seeds may have a synergistic effect with other drugs, such as chemotherapeutic agents or antibiotics, which may lead to a reduction in the therapeutic dose, may have an improved effect, and could lead to overcoming obstacles such as drug resistance. The studies provided in this review showed that NS has the potential to be a therapeutic agent both as a monotherapy and as an adjuvant. Although there are studies demonstrating the therapeutic properties of NS, there is a need for much more extensive research and more clinical trials with clearly established objectives so that the mechanism of action of the active substances in NS is much better understood. With the data provided so far, NS can be used in food and drug production in small quantities and can be administered for short periods. Further investigations may lead to an understanding of the therapeutic profile and the most effective mode of administration, as well as a clearer perspective on the toxicological profile of NS.
Keywords: Nigella sativa; analgesic; anti-inflammatory effect; antimicrobial; antioxidant; antipyretic; immunomodulator; thymol; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hamed E.S., Toaima W.I., Abd El-Aleem W.H. Impact of different planting locations on Nigella sativa L. yield in egypt. Egypt. J. Desert Res. 2023;73:23–38. doi: 10.21608/ejdr.2023.198316.1130. - DOI
-
- Ahmad R., Ahmad N., Amir M., AlJhisi F., Alamer M.H., Al-Shaban H.R., Alsultan B.M., Alsadah Z.A., Aldawood N.A., Chathoth S., et al. Variation in Nigella sativa quality and its standardization via instrumental analysis: A study based on geographical origin. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca. 2020;48:1141–1154. doi: 10.15835/nbha48311957. - DOI
-
- Hannan M.A., Rahman M.A., Sohag A.A.M., Uddin M.J., Dash R., Sikder M.H., Rahman M.S., Timalsina B., Munni Y.A., Sarker P.P., et al. Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review on Phytochemistry, Health Benefits, Molecular Pharmacology, and Safety. Nutrients. 2021;13:1784. doi: 10.3390/nu13061784. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belgaumi U., Patil S., Gandhi J., Shete A. The Many Therapeutic Applications of Nigella sativa—A Review of Literature. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2020;9:2151–2157. doi: 10.14260/jemds/2020/469. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

