Gut Microbiota and Liver Dysfunction in Sepsis: The Role of Inflammatory Mediators and Therapeutic Approaches
- PMID: 39769181
- PMCID: PMC11678143
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413415
Gut Microbiota and Liver Dysfunction in Sepsis: The Role of Inflammatory Mediators and Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
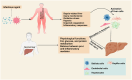
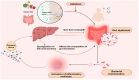
Sepsis is a life-threatening complication caused by an uncontrolled immune response to infection that can lead to multi-organ dysfunction, including liver injury. Recent research has shown the critical role of gut microbiota in sepsis pathogenesis, with the gut-liver axis playing a crucial role in disease progression. Mechanisms such as the disruption of the gut barrier and liver injury pathways mediated by cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, hydrogen sulfide (H2S). and substance P (SP) have been the focus of recent studies. Some potential biomarkers and gut microbiota-targeted therapies have shown promise as emerging tools for predicting and managing sepsis. This review describes the role of the gut-liver axis in sepsis and the potential of microbiota-targeted therapies and biomarker-driven interventions to improve sepsis outcomes.
Keywords: gut microbiota; gut–liver axis; liver; sepsis; therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RESEARCH PROGRESS ON THE ROLE OF GUT MICROBIOTA AND ITS METABOLITES IN THE OCCURRENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEPTIC-ASSOCIATED LIVER INJURY.Shock. 2025 Jan 1;63(1):4-10. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002441. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Shock. 2025. PMID: 39158846 Review.
-
Gut microbiota modulation and anti-inflammatory properties of Xuanbai Chengqi decoction in septic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113534. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113534. Epub 2020 Nov 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33137434
-
Gut-liver crosstalk in sepsis-induced liver injury.Crit Care. 2020 Oct 19;24(1):614. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03327-1. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 33076940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbe-derived betulinic acid alleviates sepsis-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting macrophage NLRP3 inflammasome in mice.mBio. 2025 Mar 12;16(3):e0302024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03020-24. Epub 2025 Jan 31. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39887250 Free PMC article.
-
Gut-liver axis in sepsis-associated liver injury: Epidemiology, challenges and clinical practice.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 7;31(1):99987. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.99987. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39777244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gastric Cancer and Microbiota: Exploring the Microbiome's Role in Carcinogenesis and Treatment Strategies.Life (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;15(7):999. doi: 10.3390/life15070999. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Unraveling Its Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Conditions.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 30;47(5):322. doi: 10.3390/cimb47050322. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699721 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.-D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rudd K.E., Johnson S.C., Agesa K.M., Shackelford K.A., Tsoi D., Kievlan D.R., Colombara D.V., Ikuta K.S., Kissoon N., Finfer S., et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395:200–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

