Chiral Amino Acids Mediate Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis of Human Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells Under Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 39769204
- PMCID: PMC11677210
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413439
Chiral Amino Acids Mediate Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis of Human Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells Under Oxidative Stress
Abstract
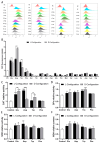
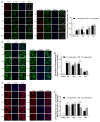
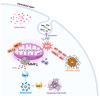
Amino acids are the basic structural units of life, and their intake levels affect disease and health. In the case of renal disease, alterations in amino acid metabolism can be used not only as a clinical indicator of renal disease but also as a therapeutic strategy. However, the biological roles and molecular mechanisms of natural chiral amino acids in human proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2) remain unclear. In this study, cell viability assays revealed that chiral acidic amino acids (Glu and Asp) and aromatic amino acids (Trp and Phe) inhibited cell growth. The molecular mechanisms indicated that cell growth was closely related to ROS levels. Specifically, chiral Glu, Asp, Trp, and Phe induced oxidative stress and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in HK-2 cells. This was manifested by elevated levels of intracellular ROS, 8-OHdG, and MDA, increased activities of antioxidant enzymes CAT, SOD, and GPx, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, increased cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration, and cell acidification. The expression levels of apoptosis-related molecules Caspase-9, Caspase-3, Cyt-C, and Bax were increased, and the expression level of anti-apoptotic molecule Bcl-2 was decreased. Moreover, L-Glu, D-Asp, L-Trp, and D-Phe exhibited a more pronounced inhibition of cell growth and elicited more substantial alterations in gene expression compared to the other configurations.
Keywords: HK-2 cells; ROS; apoptosis; chiral amino acids; mitochondria-dependent; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

