Apoptosis-Inducing and Proliferation-Inhibiting Effects of Doramectin on Mz-ChA-1 Human Cholangiocarcinoma Cells
- PMID: 39769205
- PMCID: PMC11676298
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413440
Apoptosis-Inducing and Proliferation-Inhibiting Effects of Doramectin on Mz-ChA-1 Human Cholangiocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
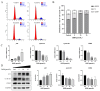
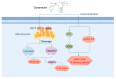
Cholangiocarcinoma is a malignant tumor that emerges in the intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile ducts. Doramectin (DOR), a third-generation derivative of avermectins (AVMs), is renowned for its low toxicity and high efficiency. However, no research has hitherto focused on the anti-cholangiocarcinoma effects of these drugs. In this study, we undertook a preliminary exploration of the mechanism through which DOR inhibits the viability of human cholangiocarcinoma cells (Mz-ChA-1) via transcriptome analysis and molecular validation at the cellular level. The results indicated that DOR could suppress the growth and proliferation of Mz-ChA-1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, it significantly diminished their migration and invasion abilities. Cell cycle analysis disclosed arrest in the G1 phase, accompanied by an increase in p21 expression and a decrease in the levels of the cyclin E1 and CDK2 proteins. Additionally, DOR induced apoptosis via the ROS-triggered mitochondrial pathway. This was attested by an elevation in the BAX/BCL-2 ratio, the activation of caspase 3/7 and the cleavage of PARP1. These mechanistic insights underscore DOR's potential as a therapeutic agent against cholangiocarcinoma.
Keywords: Mz-ChA-1; apoptosis; doramectin; proliferation-inhibiting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31870780/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21CZP002HJ05/Xiamen Southern Oceanographic Center
- 16PFW008SF15/Xiamen Southern Oceanographic Center
- TICMBR202404/Technology Innovation Center for Exploitation of Marine Biological Resources, MNR
- BHSFS002/the Beihai Pilot City Program for the National Innovative Development of the Marine Economy
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

