Regulation of Cancer Metastasis by PAK2
- PMID: 39769207
- PMCID: PMC11676821
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413443
Regulation of Cancer Metastasis by PAK2
Abstract
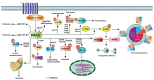
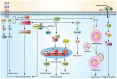
PAK2 is a serine-threonine kinase and a member of the p21-activated kinase (PAK) family. PAK2 is activated by GTP-bound rho family GTPases, Rac, and Cdc42, and it regulates actin dynamics, cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix, and cell motility. In various types of cancers, PAK2 has been implicated in the regulation of cancer cell proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis. In addition, recent studies have shown that PAK2 plays an important role in cancer cell metastasis, indicating PAK2 as a potential therapeutic target. This review discusses recent discoveries on the functions of PAK2 in the regulation of various types of cancers. A better understanding of the mechanisms of function of PAK2 will facilitate future development of cancer therapies.
Keywords: PAK2; apoptosis; cancer metastasis; cell cycle; rho family GTPases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Orton K.C., Ling J., Waskiewicz A.J., Cooper J.A., Merrick W.C., Korneeva N.L., Rhoads R.E., Sonenberg N., Traugh J.A. Phosphorylation of Mnk1 by Caspase-Activated Pak2/γ-PAK Inhibits Phosphorylation and Interaction of eIF4G with Mnk. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:38649–38657. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407337200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

