Targeting 5-HT Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 39769209
- PMCID: PMC11679250
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413446
Targeting 5-HT Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
There is increasing interest in the potential therapeutic role of 5-HT (serotonin) in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, which are characterized by the progressive degeneration and death of nerve cells. 5-HT is a vital neurotransmitter that plays a central role in regulating mood, cognition, and various physiological processes in the body. Disruptions in the 5-HT system have been linked to several neurological and psychiatric disorders, making it an attractive target for therapeutic intervention. Although the exact causes of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are not fully understood, researchers believe that regulating the 5-HT system could help alleviate symptoms and potentially slow the progression of these diseases. Here, we delve into the potential of harnessing 5-HT as a therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. It is important to note that the current clinical drugs targeting 5-HT are still limited in the treatment of these complex diseases. Therefore, further research and clinical trials are needed to evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of its clinical application.
Keywords: 5-HT; clinical trials; neurodegenerative diseases; therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
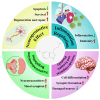
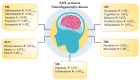
 ” indicates that the activation of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom; “
” indicates that the activation of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom; “ ” indicates that inhibition of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom.
” indicates that inhibition of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom.References
-
- Pentkowski N.S., Rogge-Obando K.K., Donaldson T.N., Bouquin S.J., Clark B.J. Anxiety and Alzheimer’s disease: Behavioral analysis and neural basis in rodent models of Alzheimer’s-related neuropathology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021;127:647–658. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.05.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

