Chronic Oxidative Stress and Stress Granule Formation in UBQLN2 ALS Neurons: Insights into Neuronal Degeneration and Potential Therapeutic Targets
- PMID: 39769213
- PMCID: PMC11678478
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413448
Chronic Oxidative Stress and Stress Granule Formation in UBQLN2 ALS Neurons: Insights into Neuronal Degeneration and Potential Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
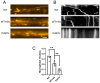
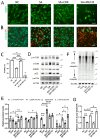
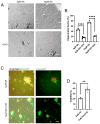
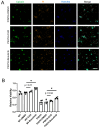
The pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases results from the interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Aging and chronic oxidative stress are critical contributors to neurodegeneration. UBQLN2, a ubiquitin-related protein, aids in protein degradation and protects against oxidative stress. In ALS neurons harboring UBQLN2 mutations, oxidative stress accelerates pathological changes, yet the precise mechanisms remain unclear. Using induced motor neurons (iMNs) derived from UBQLN2 P497H iPSCs, we observed ALS-like phenotypes, including TDP-43 mislocalization, increased cell death, and reduced viability. Sodium arsenite (SA)-induced oxidative stress triggered stress granule formation, while autophagy dysfunction exacerbated neuronal degeneration. CHX and bosutinib treatments reduced ubiquitinated protein accumulation and alleviated degeneration, highlighting potential therapeutic pathways. These findings emphasize the role of chronic oxidative stress and stress granule formation in UBQLN2 ALS, offering insights into novel therapeutic targets.
Keywords: ALS; UBQLN2; motor neurons; neurodegenerative diseases; oxidative stress; stress granule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Belbasis L., Bellou V., Evangelou E. Environmental Risk Factors and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: An Umbrella Review and Critical Assessment of Current Evidence from Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies. Neuroepidemiology. 2016;46:96–105. doi: 10.1159/000443146. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

