Unveiling Secondary Mutations in Blended Phenotypes: Dual ERCC4 and OTOA Pathogenic Variants Through WES Analysis
- PMID: 39769235
- PMCID: PMC11679737
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413471
Unveiling Secondary Mutations in Blended Phenotypes: Dual ERCC4 and OTOA Pathogenic Variants Through WES Analysis
Abstract
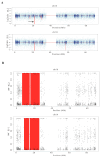
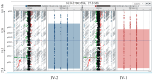
This study describes two siblings from consanguineous parents who exhibit intellectual disability, microcephaly, photosensitivity, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, numerous freckles, and other clinical features that suggest a potential disruption of the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway. Whole exome sequencing (WES) identified a novel homozygous missense variant in the ERCC4 gene, which was predicted to be pathogenic. However, a subsequent peculiar audiometric finding prompted further investigation, revealing a homozygous deletion in the OTOA gene linked to neurosensorial hearing loss. Both variants were located within a run of homozygosity (ROH) on chromosome 16p13.12-p12.2, implicating a complex genetic basis for the observed phenotype. While this study reports a potentially novel ERCC4 variant, it underscores the importance of comprehensive analysis and deep phenotyping in WES data to improve diagnostic accuracy. Our findings advocate for an expanded approach in WES analysis, ensuring more precise diagnoses and improved genetic counseling, particularly when specialized tests for structural variant analysis are unavailable.
Keywords: ERCC4; OTOA; blended phenotypes; dual diagnoses; run of homozygosity; whole exome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rosina E., Pezzani L., Pezzoli L., Marchetti D., Bellini M., Pilotta A., Calabrese O., Nicastro E., Cirillo F., Cereda A., et al. Atypical, Composite, or Blended Phenotypes: How Different Molecular Mechanisms Could Associate in Double-Diagnosed Patients. Genes. 2022;13:1275. doi: 10.3390/genes13071275. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

