Epicatechin Influence on Biochemical Modification of Human Erythrocyte Metabolism and Membrane Integrity
- PMID: 39769244
- PMCID: PMC11677421
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413481
Epicatechin Influence on Biochemical Modification of Human Erythrocyte Metabolism and Membrane Integrity
Abstract
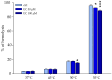
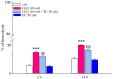
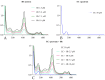
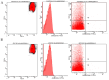
Red blood cells (RBCs) are the main cells of the blood, perform numerous functions within the body and are in continuous contact with endogenous and exogenous molecules. In this context, the study aims to investigate the effect of epicatechin (EC) (flavan-3-ols) on the erythrocytes, analyzing the protective effect of the molecule and the action exerted on metabolism and RBC membrane. The effect of EC on RBC viability has been evaluated through the change in hemolysis and methemoglobin, assessing caspase 3 activity and performing a cytofluorometric analysis. Next, the impact of the molecule on RBC metabolism was assessed by measuring anion flux kinetics, ATP production, and phosphatase activity. Finally, an evaluation of the potential protection against different stressors was performed. Our results show no detrimental effects of EC on RBCs (no change in hemolysis or methemoglobin and no caspase 3 activation recorded); rather, a protective effect was recorded given the reduction in hemolysis induced by hydrogen peroxide treatment and temperature increase. The increase in anion exchange and intracellular ATP values, with the inhibition of phosphatase PTP1B activity, highlights several biochemical alterations induced by EC. The present results contribute to clarifying the influence of EC on RBCs, confirming the beneficial effects of catechins.
Keywords: Band-3 protein; anion exchange; antioxidant systems; epicatechin; erythrocyte metabolism; red blood cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Influence of cocoa flavanols and procyanidins on free radical-induced human erythrocyte hemolysis.Clin Dev Immunol. 2005 Mar;12(1):27-34. doi: 10.1080/17402520512331329514. Clin Dev Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15712596 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biobased epicatechin conjugates protect erythrocytes and nontumoral cell lines from H2O2-induced oxidative stress.J Agric Food Chem. 2009 May 27;57(10):4459-65. doi: 10.1021/jf900240a. Epub 2009 Apr 10. J Agric Food Chem. 2009. PMID: 19361155
-
Mechanisms Underlying the Effects of Chloroquine on Red Blood Cells Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 11;25(12):6424. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126424. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928131 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Catechins with Human Erythrocytes.Molecules. 2020 Mar 24;25(6):1456. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061456. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32213847 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Sepsis on the Erythrocyte.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 8;18(9):1932. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091932. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28885563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Morus alba Leaves Extract on Human Erythrocytes.Biology (Basel). 2025 Aug 5;14(8):1005. doi: 10.3390/biology14081005. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40906167 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

