Systematic Review of IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-15, and IL-18 Gene Polymorphisms and Meta-Analysis of IL-6 Variant and Its Association with Overweight and Obesity Risk in Men
- PMID: 39769263
- PMCID: PMC11679641
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413501
Systematic Review of IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-15, and IL-18 Gene Polymorphisms and Meta-Analysis of IL-6 Variant and Its Association with Overweight and Obesity Risk in Men
Abstract
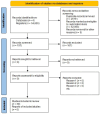
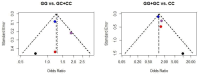
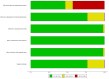
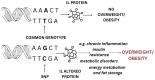
Obesity is a complex health risk influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This review systematically assessed the association between interleukin gene polymorphisms (rs16944, rs17561, rs1143623, rs1143633, rs1143634, rs1800587, rs2234677, and rs4848306), IL-4 (rs180275, rs1805010, IL-6 rs13306435, rs1800795, rs1800796, rs1800797, rs2228145, rs2228145, rs2229238, and rs4845623), IL-10 (rs1518110, rs1518111, rs1800871, rs1800872, rs1800896, rs1878672, rs2834167, rs3024491, rs3024496, rs3024498, and rs3024505), IL-15 (rs3136617, rs3136618, and rs2296135), and IL-18 (rs187238, rs1946518, rs2272127, rs2293225, and rs7559479) and the risk of overweight and obesity in adults, focusing on IL-6 rs1800795 through a meta-analysis. The focus on IL-6 in this review arises from its pleiotropic nature and unclear effect on obesity risk. The review included studies published from 1998 to 2023, sourced from Science Direct, EBSCOhost, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. Bias was assessed with the Cochrane Collaboration tool, and funnel plots were used for publication bias. Results were synthesized into pooled odds ratios (ORs) and confidence intervals (CIs). Thirty studies comprising approximately 29,998 participants were included. The selection criteria required that the articles include participants who were overweight or obese, and this condition needed to be linked to IL polymorphisms. In a meta-analysis, in the dominant model, the pooled OR was 1.26 (95% CI 1.08 to 1.47), indicating those with the GC/CC genotype for IL-6 rs1800795 are 1.26 times more likely to be overweight/obese than GG genotype carriers. For the recessive model, the OR was 1.25 (95% CI 1.04 to 1.51). The overdominant model showed no significant association (OR 1.08, 95% CI 0.94 to 1.25). Interleukin gene variation, particularly the IL-6 rs1800795 variant, is modestly associated with obesity risk. This suggests that other factors, such as the environment, also play a role in obesity. Thus, individuals with this particular IL-6 variant may have a slightly higher likelihood of being overweight or obese compared to those without it, but this is just one of many factors influencing obesity risk.
Keywords: genetic variant; interleukin; obesity; overweight; polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

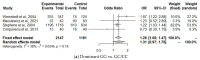
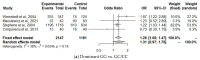
Similar articles
-
Influence of interleukin gene polymorphisms on development of acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Oct;40(10):5931-41. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2700-6. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24072654
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Cytokine Gene Variants as Predisposing Factors for the Development and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 19;14(12):1631. doi: 10.3390/biom14121631. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766338 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The interleukin gene landscape: understanding its influence on inflammatory mechanisms in apical periodontitis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Apr 7;52(1):365. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10477-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40192910 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. 2023. [(accessed on 7 November 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017;390:2627–2642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

