Precise and Accurate DNA-3'/5-Ends Polishing with Thermus thermophilus Phage vb_Tt72 DNA Polymerase
- PMID: 39769307
- PMCID: PMC11677593
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413544
Precise and Accurate DNA-3'/5-Ends Polishing with Thermus thermophilus Phage vb_Tt72 DNA Polymerase
Abstract
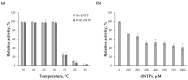
Tt72 DNA polymerase is a newly characterized PolA-type thermostable enzyme derived from the Thermus thermophilus phage vB_Tt72. The enzyme demonstrates strong 3'→5' exonucleolytic proofreading activity, even in the presence of 1 mM dNTPs. In this study, we examined how the exonucleolytic activity of Tt72 DNA polymerase affects the fidelity of DNA synthesis. Using a plasmid-based lacZα gene complementation assay, we determined that the enzyme's mutation frequency was 2.06 × 10-3, corresponding to an error rate of 1.41 × 10-5. For the exonuclease-deficient variant, the mutation frequency increased to 6.23 × 10-3, with an associated error rate of 4.29 × 10-5. The enzyme retained 3'→5' exonucleolytic activity at temperatures up to 70 °C but lost it after 10 min of incubation at temperatures above 75 °C. Additionally, we demonstrated that Tt72 DNA polymerase efficiently processes 3'/5'-overhangs and removes a single-nucleotide 3'-dA overhang from PCR products at 55 °C. These characteristics make Tt72 DNA polymerase well suited for specialized molecular cloning applications.
Keywords: 3′→5′ exonuclease activity; PolA-type enzyme; molecular cloning; proofreading.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. As expected, the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Kornberg A., Baker T.A. DNA Replication. 2nd ed. Freeman; New York, NY, USA: 1992.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

