Essential Role of Cortactin in Myogenic Differentiation: Regulating Actin Dynamics and Myocardin-Related Transcription Factor A-Serum Response Factor (MRTFA-SRF) Signaling
- PMID: 39769327
- PMCID: PMC11677934
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413564
Essential Role of Cortactin in Myogenic Differentiation: Regulating Actin Dynamics and Myocardin-Related Transcription Factor A-Serum Response Factor (MRTFA-SRF) Signaling
Abstract
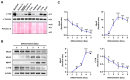
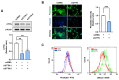
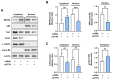
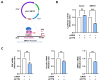
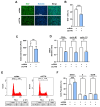
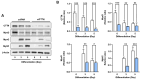
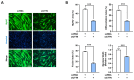
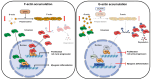
Cortactin (CTTN) is an actin-binding protein regulating actin polymerization and stabilization, which are vital processes for maintaining skeletal muscle homeostasis. Despite the established function of CTTN in actin cytoskeletal dynamics, its role in the myogenic differentiation of progenitor cells remains largely unexplored. In this study, we investigated the role of CTTN in the myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts by analyzing its effects on actin cytoskeletal remodeling, myocardin-related transcription factor A (MRTFA) nuclear translocation, serum response factor (SRF) activation, expression of myogenic transcription factors, and myotube formation. CTTN expression declined during myogenic differentiation, paralleling the reduction in MyoD, suggesting a potential role in the early stages of myogenesis. We also found that CTTN knockdown in C2C12 myoblasts reduced filamentous actin, enhanced globular actin levels, and inhibited the nuclear translocation of MRTFA, resulting in suppressed SRF activity. This led to the subsequent downregulation of myogenic regulatory factors, such as MyoD and MyoG. Furthermore, CTTN knockdown reduced the nuclear localization of YAP1, a mechanosensitive transcription factor, further supporting its regulatory roles in cell cycle and proliferation. Consequently, CTTN depletion impeded proliferation, differentiation, and myotube formation in C2C12 myoblasts, highlighting its dual role in the coordination of cell cycle regulation and myogenic differentiation of progenitor cells during myogenesis. This study identifies CTTN as an essential regulator of myogenic differentiation via affecting the actin remodeling-MRTFA-SRF signaling axis and cell proliferation.
Keywords: MRTFA; SRF; YAP1; actin remodeling; cortactin; mechanotransduction; myogenic differentiation; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

