The Potential Regulatory Role of Ferroptosis in Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption
- PMID: 39769377
- PMCID: PMC11728003
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413617
The Potential Regulatory Role of Ferroptosis in Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption
Abstract
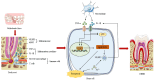
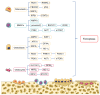
People, in increasing numbers, are seeking orthodontic treatment to correct malocclusion, while some of them are suffering from orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption (OIIRR). Recent evidence suggests that the immune-inflammatory response occurring during bone remodeling may be responsible for OIIRR. Ferroptosis, a new type of programmed cell death (PCD), has been found to have a close interrelation with inflammation during disease progression. While ferroptosis has been extensively studied in bone-related diseases, its role in OIIRR is poorly understood. Considering that the tooth root shares a lot of similar characteristics with bone, it is reasonable to hypothesize that ferroptosis contributes to the development of OIIRR. Nevertheless, direct evidence supporting this theory is currently lacking. In this review, we introduced ferroptosis and elucidated the mechanisms underlying orthodontic tooth movement (OTM) and OIIRR, with a special focus on the pivotal role inflammation plays in these processes. Additionally, we covered recent research exploring the connections between inflammation and ferroptosis. Lastly, we emphasized the important regulatory function of ferroptosis in bone homeostasis. Further investigations are required to clarify the modulation mechanisms of ferroptosis in OIIRR and to develop novel and potential therapeutic strategies for the management of OIIRR.
Keywords: ferroptosis; inflammation; orthodontic tooth movement; orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nishioka M., Ioi H., Nakata S., Nakasima A., Counts A. Root resorption and immune system factors in the Japanese. Angle Orthod. 2006;76:103–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

