Efficient mRNA Delivery In Vitro and In Vivo Using a Polycharged Biodegradable Nanomaterial
- PMID: 39769382
- PMCID: PMC11728123
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413620
Efficient mRNA Delivery In Vitro and In Vivo Using a Polycharged Biodegradable Nanomaterial
Abstract
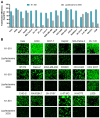
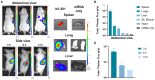
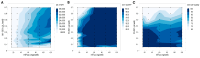
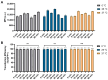
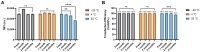
As RNA rises as one of the most significant modalities for clinical applications and life science research, efficient tools for delivering and integrating RNA molecules into biological systems become essential. Herein, we report a formulation using a polycharged biodegradable nano-carrier, N1-501, which demonstrates superior efficiency and versatility in mRNA encapsulation and delivery in both cell and animal models. N1-501 is a polymeric material designed to function through a facile one-step formulation process suitable for various research settings. Its capability for mRNA transfection is investigated across a wide range of mRNA doses and in different biological models, including 18 tested cell lines and mouse models. This study also comprehensively analyzes N1-501's application for mRNA transfection by examining factors such as buffer composition and pH, incubation condition, and media type. Additionally, N1-501's superior in vivo mRNA transfection capability ensures its potential as an efficient and consistent tool for advancing mRNA-based therapies and genetic research.
Keywords: RNA research; RNA therapeutics; RNA translation; gene delivery; gene editing; mRNA transfection; protein translation; targeted delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
All Authors are employees of or advisors to N1 Life, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

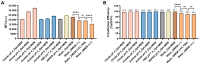
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

