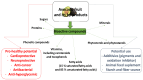
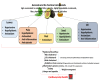
The Pulp, Peel, Seed, and Food Products of Persea americana as Sources of Bioactive Phytochemicals with Cardioprotective Properties: A Review
- PMID: 39769384
- PMCID: PMC11728118
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413622
The Pulp, Peel, Seed, and Food Products of Persea americana as Sources of Bioactive Phytochemicals with Cardioprotective Properties: A Review
Abstract
Botanically speaking, avocado (Persea americana) is a fruit. It consists of a single large seed surrounded by a creamy, smooth-textured edible mesocarp or pulp covered by a thick, bumpy skin. Avocado is a nutrient-dense fruit, containing a range of bioactive compounds which have been independently associated with cardiovascular health. These compounds have been obtained from the pulp, peel, and seed. This narrative review summarizes the current understanding of the cardioprotective potential of avocado fruit, especially the pulp and seed, and its food products, and examines the biological mechanism behind it.
Keywords: avocado; cardiovascular disease; fatty acid; phenolic compound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Avocado (Persea americana) seed as a source of bioactive phytochemicals.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(34):6133-40. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319340007. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448442 Review.
-
Characterization of physicochemical properties, fatty acids, flavor volatiles and phenolic compounds of avocado varieties.Food Chem. 2025 Aug 1;482:143533. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143533. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40220553
-
Avocado fruit and by-products as potential sources of bioactive compounds.Food Res Int. 2020 Dec;138(Pt A):109774. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109774. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33292952 Review.
-
Valorization of avocado seeds with antioxidant capacity using pressurized hot water extraction.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 29;12(1):13036. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17326-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35906278 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Methanolic Extract of Avocado Persea americana (var. Colinred) Peel on Paraquat-Induced Locomotor Impairment, Lipid Peroxidation and Shortage of Life Span in Transgenic knockdown Parkin Drosophila melanogaster.Neurochem Res. 2019 Aug;44(8):1986-1998. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02835-z. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 31309393
Cited by
-
Turning Waste into Taste: Effective Upcycling of By-Products for Innovative Food Solutions§.Food Technol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;63(2):190-205. doi: 10.17113/ftb.63.02.25.8962. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40735152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persea americana Peel: A Promising Source of Nutraceutical for the Mitigation of Cardiovascular Risk in Arthritic Rats Through the Gut-Joint Axis.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 16;15(4):590. doi: 10.3390/biom15040590. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305360 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds, Technological Advances, and Sustainable Applications of Avocado (Persea americana Mill.): A Critical Review.Foods. 2025 Aug 6;14(15):2746. doi: 10.3390/foods14152746. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40807683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Aging Potential of Avocado Oil via Its Antioxidant Effects.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 12;18(2):246. doi: 10.3390/ph18020246. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ochoa-Zarzosa A., Baez-Magana M., Guzman-Rodriguez J.J., Flores-Alvarez J.L., Lara-Marquez M., Zavala-Guerrero B., Salgado-Garciglia R., Lopez-Gomez R., Lopez-Meza J.E. Bioactive molecules from native Mexican avocado fruit (Persea americana var. drymifolia): A review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2021;76:133–142. doi: 10.1007/s11130-021-00887-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources