The Pulp, Peel, Seed, and Food Products of Persea americana as Sources of Bioactive Phytochemicals with Cardioprotective Properties: A Review
- PMID: 39769384
- PMCID: PMC11728118
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413622
The Pulp, Peel, Seed, and Food Products of Persea americana as Sources of Bioactive Phytochemicals with Cardioprotective Properties: A Review
Abstract
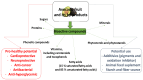
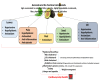
Botanically speaking, avocado (Persea americana) is a fruit. It consists of a single large seed surrounded by a creamy, smooth-textured edible mesocarp or pulp covered by a thick, bumpy skin. Avocado is a nutrient-dense fruit, containing a range of bioactive compounds which have been independently associated with cardiovascular health. These compounds have been obtained from the pulp, peel, and seed. This narrative review summarizes the current understanding of the cardioprotective potential of avocado fruit, especially the pulp and seed, and its food products, and examines the biological mechanism behind it.
Keywords: avocado; cardiovascular disease; fatty acid; phenolic compound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ochoa-Zarzosa A., Baez-Magana M., Guzman-Rodriguez J.J., Flores-Alvarez J.L., Lara-Marquez M., Zavala-Guerrero B., Salgado-Garciglia R., Lopez-Gomez R., Lopez-Meza J.E. Bioactive molecules from native Mexican avocado fruit (Persea americana var. drymifolia): A review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2021;76:133–142. doi: 10.1007/s11130-021-00887-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources