Different Cytotoxic Effects of Cisplatin on Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines
- PMID: 39769425
- PMCID: PMC11727771
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413662
Different Cytotoxic Effects of Cisplatin on Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines
Abstract
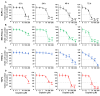
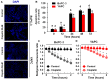
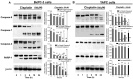
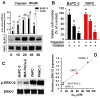
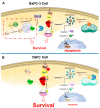
This study examined the response to cisplatin in BxPC-3, Mia-Paca-2, PANC-1, and YAPC pancreatic cancer lines with different genotypic and phenotypic characteristics, and the mechanisms associated with their resistance. BxPC-3 and MIA-PaCa-2 cell lines were the most sensitive to cisplatin, while YAPC and PANC-1 were more resistant. Consistently, in cisplatin-treated BxPC-3 cells, the cleavage patterns of pro-caspase-9, -7, -3, and PARP-1 demonstrated that they were more sensitive than YAPC cells. The autophagic pathway, promoting cisplatin resistance, was active in BxPC-3 cells, as demonstrated by the time-dependent conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II, whereas it was not activated in YAPC cells. In cisplatin-treated BxPC-3 cells, Bcl-2 decreased, while Beclin-1, Atg-3, and Atg-5 increased along with JNK1/2 phosphorylation. Basal levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 in each cell line were positively correlated with cisplatin IC50 values, and cisplatin caused the activation of ERK1/2 in BxPC-3 and YAPC cells. Furthermore, ERK1/2 pharmacological inactivation increased cisplatin lethality in both BxPC-3 and YAPC cells, suggesting that p-ERK1/2 may be related to cisplatin resistance of PDAC cells. Different mechanisms and strategies are generally required to acquire drug resistance. Here, we partially explain the other response to cisplatin of BxPC-3 and YAPC cell lines by relating it to the role of ERK pathway.
Keywords: apoptosis; cisplatin; cytotoxicity; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Grossberg A.J., Chu L.C., Deig C.R., Fishman E.K., Hwang W.L., Maitra A., Marks D.L., Mehta A., Nabavizadeh N., Simeone D.M., et al. Multidisciplinary standards of care and recent progress in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020;70:375–403. doi: 10.3322/caac.21626. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

