The Role of ctDNA in the Management of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the AI and NGS Era
- PMID: 39769431
- PMCID: PMC11727717
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413669
The Role of ctDNA in the Management of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the AI and NGS Era
Abstract
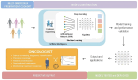
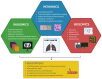
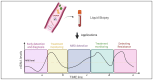
Liquid biopsy (LB) involves the analysis of circulating tumour-derived DNA (ctDNA), providing a minimally invasive method for gathering both quantitative and qualitative information. Genomic analysis of ctDNA through next-generation sequencing (NGS) enables comprehensive genetic profiling of tumours, including non-driver alterations that offer prognostic insights. LB can be applied in both early-stage disease settings, for the diagnosis and monitoring of minimal residual disease (MRD), and advanced disease settings, for monitoring treatment response and understanding the mechanisms behind disease progression and tumour heterogeneity. Currently, LB has limited use in clinical practice, primarily due to its significant costs, limited diagnostic yield, and uncertain prognostic role. The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in the medical field is a promising approach to processing extensive information and applying it to individual cases to enhance therapeutic decision-making and refine risk assessment.
Keywords: NGS; NSCLC; artificial intelligence; ctDNA; liquid biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
M.M. was member of MSD Adviser Board. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hendriks L.E., Kerr K.M., Menis J., Mok T.S., Nestle U., Passaro A., Peters S., Planchard D., Smit E.F., Solomon B.J., et al. Non-oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023;34:358–376. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.12.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

