The Impact of Alkaline Stress on Plant Growth and Its Alkaline Resistance Mechanisms
- PMID: 39769481
- PMCID: PMC11677074
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413719
The Impact of Alkaline Stress on Plant Growth and Its Alkaline Resistance Mechanisms
Abstract
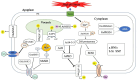
Alkaline stress can induce significant injury to plants, resulting in a range of negative effects, including ion toxicity, oxidative stress, and damage from high pH values. These stress factors can substantially affect normal plant growth and development, as well as yield and quality loss. To counteract alkaline stress, plants have developed a range of defense strategies, enabling them to adapt and thrive in challenging environments. These defense mechanisms operate at multiple levels such as morphological, physiological, biochemical, and molecular. The continuous advancement of genetic engineering has enabled significant breakthroughs in enhancing plant alkali resistance through human intervention. This research provides a scientific basis for crop production and ecological environment construction, and also promotes the effective development and utilization of saline-alkali lands, improving the sustainability of agricultural production.
Keywords: agricultural production; alkaline stress; high pH; plant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Xv Z.Q., Xia G.M. Research progress on the causes, characteristics and remediation measures of soda saline-alkali soil in the songnen plain. Soil Water Conserv. China. 2018;02:54–59+69. doi: 10.14123/j.cnki.swcc.2018.0047. - DOI
-
- Wang S.J., Chen Q., Li Y., Zhuo Y.Q., Xu L.Z. Research on saline-alkali soil amelioration with FGD gypsum. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017;121:82–92. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.04.005. - DOI
-
- Pearce F. The $27 billion cost of salt poisoning. New Sci. 2014;224:10. doi: 10.1016/S0262-4079(14)62072-8. - DOI
-
- Guo S.S., Ruan B.Q., Chen H.R., Guan X.Y., Wang S.L., Xu N.N., Li Y.P. Characterizing the spatiotemporal evolution of soil salinization in Hetao Irrigation District (China) using a remote sensing approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018;39:6805–6825. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2018.1466076. - DOI
-
- Yang C.W., Shi D.C., Wang D.L. Comparative effects of salt and alkali stresses on growth, osmotic adjustment and ionic balance of an alkali-resistant halophyte Suaeda glauca (Bge.) Plant Growth Regul. 2008;56:179–190. doi: 10.1007/s10725-008-9299-y. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

