Optimizing Yeast Homologous Recombination for Splicing Large Coronavirus Genome Fragments
- PMID: 39769503
- PMCID: PMC11677428
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252413742
Optimizing Yeast Homologous Recombination for Splicing Large Coronavirus Genome Fragments
Abstract
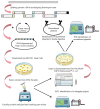
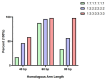
Reverse genetics is a useful tool for studying viruses and developing vaccines for coronaviruses. However, constructing and manipulating the coronavirus genome in Escherichia coli can be time-consuming and challenging due to its large size and instability. Homologous recombination, a genetic manipulation mechanism found in organisms, is essential for DNA repair, gene recombination, and genetic engineering. In yeast, particularly Saccharomyces cerevisiae, homologous recombination technology is commonly used for constructing gene expression plasmids and genome editing. In this study, we successfully split and spliced a 30 kb viral genome fragment using yeast homologous recombination. By optimizing the program parameters, such as homologous arm lengths and fragment-to-vector ratios, we achieved a splicing efficiency of up to 97.9%. The optimal parameters selected were a 60 bp homologous sequence size and a vector fragment ratio of 1:2:2:2:2:2 for yeast homologous recombination of large DNA fragments.
Keywords: DNA assembly; automated splicing; reverse genetics; synthetic biology; yeast homologous recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

