Release and Disintegration Properties of Poly(lactic Acid) Films with Allyl Isothiocyanate-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Active Food Packaging
- PMID: 39769948
- PMCID: PMC11677350
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29245859
Release and Disintegration Properties of Poly(lactic Acid) Films with Allyl Isothiocyanate-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Active Food Packaging
Abstract
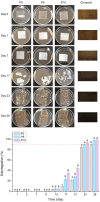
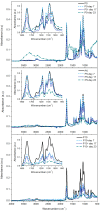
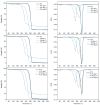
This study aimed to enhance the properties and compostability of active poly(lactic acid) (PLA) films by incorporating β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) inclusion complexes with allyl isothiocyanate (AITC). Films were prepared using melt extrusion and characterized based on their structural, chemical, morphological, thermal, and barrier properties. These inclusion complexes improved the thermal stability and moisture absorption of films, enhancing disintegration under composting conditions. The release of AITC in the vapor phase was responsive to relative humidity, maintaining the antimicrobial functionality at low values and releasing effectively at higher humidity levels, with a maximum release at 100%. Incorporating 5% and 10% β-CD:AITC complexes accelerated disintegration under composting conditions, reducing the time by 5 days for disintegration compared to pure PLA, achieving up to 90% in 23 days. These results, with a general improvement in functional properties, suggest that PLA films with β-CD:AITC are promising for developing sustainable, biodegradable antimicrobial packaging solutions for food applications.
Keywords: PLA; active food packaging; allyl isothiocyanate; disintegration; release; β-cyclodextrin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lombardi A., Fochetti A., Vignolini P., Campo M., Durazzo A., Lucarini M., Puglia D., Luzi F., Papalini M., Renzi M., et al. Natural Active Ingredients for Poly (Lactic Acid)-Based Materials: State of the Art and Perspectives. Antioxidants. 2022;11:2074. doi: 10.3390/antiox11102074. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siddiqui S.A., Singh S., Bahmid N.A., Mehany T., Shyu D.J.H., Assadpour E., Malekjani N., Castro-Muñoz R., Jafari S.M. Release of Encapsulated Bioactive Compounds from Active Packaging/Coating Materials and Its Modeling: A Systematic Review. Colloids Interfaces. 2023;7:25. doi: 10.3390/colloids7020025. - DOI
-
- Westlake J.R., Tran M.W., Jiang Y., Zhang X., Burrows A.D., Xie M. Biodegradable Biopolymers for Active Packaging: Demand, Development and Directions. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023;1:50–72. doi: 10.1039/D2FB00004K. - DOI
-
- Westlake J.R., Tran M.W., Jiang Y., Zhang X., Burrows A.D., Xie M. Biodegradable Active Packaging with Controlled Release: Principles, Progress, and Prospects. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022;2:1166–1183. doi: 10.1021/acsfoodscitech.2c00070. - DOI
-
- Saifullah M.M., Shishir M.R.I.M.R.I., Ferdowsi R., Tanver Rahman M.R.M.R., Van Vuong Q. Micro and Nano Encapsulation, Retention and Controlled Release of Flavor and Aroma Compounds: A Critical Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019;86:230–251. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.02.030. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

