Cost-Effective Bioimpedance Spectroscopy System for Monitoring Syncytialization In Vitro: Experimental and Numerical Validation of BeWo Cell Fusion
- PMID: 39770259
- PMCID: PMC11678286
- DOI: 10.3390/mi15121506
Cost-Effective Bioimpedance Spectroscopy System for Monitoring Syncytialization In Vitro: Experimental and Numerical Validation of BeWo Cell Fusion
Abstract
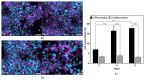
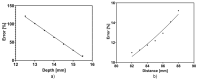
The placenta plays a critical role in nutrient and oxygen exchange during pregnancy, yet the effects of medicinal drugs on this selective barrier remain poorly understood. To overcome this, this study presents a cost-effective bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) system to assess tight junction integrity and monolayer formation in BeWo b30 cells, a widely used model of the multinucleated maternal-fetal exchange surface of the placental barrier. Cells were cultured on collagen-coated porous membranes and treated with forskolin to induce controlled syncytialization. Electrical impedance was measured using an entry level impedance analyzer, while immunofluorescence staining was used to confirm monolayer formation and syncytialization. The measurements and staining confirmed the formation of a confluent monolayer on day 4. In fact, the electrical resistance tripled for treated samples indicating a more electrically restrictive barrier. This resistance remained constant for treated samples reflecting the intact barrier's integrity over the next 3 days. The measurements show that, on day 4, the electrical capacitance of the cells decreased for the treated samples as opposed to the untreated samples. This reflects that the surface area of the BeWo b30 cells decreased when the samples were treated with forskolin. Finally, a COMSOL model was developed to explore the effects of electrode positioning, depth, and distance on TEER measurements, explaining discrepancies in the literature. In fact, there was a substantial 97% and 39.4% difference in the obtained TEER values. This study demonstrates the AD2 device's feasibility for monitoring placental barrier integrity and emphasizes the need for standardized setups for comparable results. The system can hence be used to analyze drug effects and nutrient transfer across the placental barrier.
Keywords: COMSOL (Version 6.2) multiphysics; bioimpedance spectroscopy; electrical capacitance; syncytiotrophoblast; transepithelial/transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wong M.K. Doctoral Dissertation. McMaster University; Hamilton, Canada: 2020. The Design and Characterization of Microphysiological Platforms to Model the Human Placenta.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

