A Novel Microfluidic Platform for Personalized Anticancer Drug Screening Through Image Analysis
- PMID: 39770275
- PMCID: PMC11677617
- DOI: 10.3390/mi15121521
A Novel Microfluidic Platform for Personalized Anticancer Drug Screening Through Image Analysis
Abstract
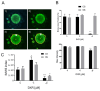
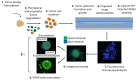
The advancement of personalized treatments in oncology has garnered increasing attention, particularly for rare and aggressive cancer with low survival rates like the bone tumors osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma. This study introduces a novel PDMS-agarose microfluidic device tailored for generating patient-derived tumor spheroids and serving as a reliable tool for personalized drug screening. Using this platform in tandem with a custom imaging index, we evaluated the impact of the anticancer agent doxorubicin on spheroids from both tumor types. The device produces 20 spheroids, each around 300 µm in diameter, within a 24 h timeframe, facilitating assessments of characteristics and reproducibility. Following spheroid generation, we measured patient-derived spheroid diameters in bright-field images, calcein AM-positive areas/volume, and the binary fraction area, a metric analyzing fluorescence intensity. By employing a specially developed equation that combines viability signal extension and intensity, we observed a substantial decrease in spheroid viability of around 75% for both sarcomas at the highest dosage (10 µM). Osteosarcoma spheroids exhibited greater sensitivity to doxorubicin than chondrosarcoma spheroids within 48 h. This approach provides a reliable in vitro model for aggressive sarcomas, representing a personalized approach for drug screening that could lead to more effective cancer treatments tailored to individual patients, despite some implementation challenges.
Keywords: chondrosarcoma; drug screening; microfluidics; osteosarcoma; personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
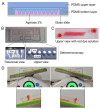
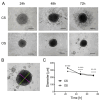
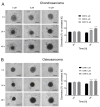
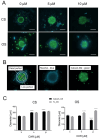
Similar articles
-
Uniform Tumor Spheroids on Surface-Optimized Microfluidic Biochips for Reproducible Drug Screening and Personalized Medicine.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Apr 9;13(4):587. doi: 10.3390/mi13040587. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35457892 Free PMC article.
-
Do Patient-derived Spheroid Culture Models Have Relevance in Chondrosarcoma Research?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021 Mar 1;479(3):477-490. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001317. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021. PMID: 32469486 Free PMC article.
-
3D stem-like spheroids-on-a-chip for personalized combinatorial drug testing in oral cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jun 18;22(1):344. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02625-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38890730 Free PMC article.
-
Spheroid-Hydrogel-Integrated Biomimetic System: A New Frontier in Advanced Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Technology.Cells Tissues Organs. 2025;214(2):128-147. doi: 10.1159/000541416. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Cells Tissues Organs. 2025. PMID: 39265553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Patient-derived 3D Micro Cancer Approach for Drug Screen in Personalized Cancer Medicine.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2025;25(2):118-130. doi: 10.2174/0115680096285910240206044830. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 38445692 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Microfluidic Ion-Exchange Optode System for Point-of-Care Determination of Sodium Concentration in Serum.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 12;15(2):104. doi: 10.3390/bios15020104. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strianese O., Rizzo F., Ciccarelli M., Galasso G., D’Agostino Y., Salvati A., Del Giudice C., Tesorio P., Rusciano M.R. Precision and Personalized Medicine: How Genomic Approach Improves the Management of Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Disease. Genes. 2020;11:747. doi: 10.3390/genes11070747. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

