Development of a Quadruplex RT-qPCR for the Detection of Porcine Astrovirus, Porcine Sapovirus, Porcine Norovirus, and Porcine Rotavirus A
- PMID: 39770312
- PMCID: PMC11728830
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13121052
Development of a Quadruplex RT-qPCR for the Detection of Porcine Astrovirus, Porcine Sapovirus, Porcine Norovirus, and Porcine Rotavirus A
Abstract
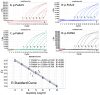
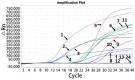
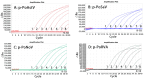
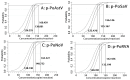
Porcine astrovirus (PoAstV), porcine sapovirus (PoSaV), porcine norovirus (PoNoV), and porcine rotavirus A (PoRVA) are newly discovered important porcine diarrhea viruses with a wide range of hosts and zoonotic potential, and their co-infections are often found in pig herds. In this study, the specific primers and probes were designed targeting the ORF1 gene of PoAstV, PoSaV, and PoNoV, and the VP6 gene of PoRVA. The recombinant standard plasmids were constructed, the reaction conditions (concentration of primers and probes, annealing temperature, and reaction cycle) were optimized, and the specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility were analyzed to establish a quadruplex real-time quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) assay for the detection of these four diarrheal viruses. The results demonstrated that the assay effectively tested PoAstV, PoSaV, PoNoV, and PoRVA without cross-reactivity with other swine viruses, and had limits of detection (LODs) of 138.001, 135.167, 140.732, and 132.199 (copies/reaction) for PoAstV, PoSaV, PoNoV, and PoRVA, respectively, exhibiting high specificity and sensitivity. Additionally, it displayed good reproducibility, with coefficients of variation (CVs) of 0.09-1.24% for intra-assay and 0.08-1.03% for inter-assay. The 1578 clinical fecal samples from 14 cities in Guangxi Province, China, were analyzed via the developed assay. The results indicated that the clinical samples from Guangxi Province exhibited the prevalence of PoAstV (35.93%, 567/1578), PoSaV (8.37%, 132/1578), PoNoV (2.98%, 47/1578), and PoRVA (14.32%, 226/1578), and had a notable incidence of mixed infections of 18.31% (289/1578). Simultaneously, the 1578 clinical samples were analyzed with the previously established assays, and the coincidence rates of these two approaches exceeded 99.43%. This study developed an efficient and precise diagnostic method for the detection and differentiation of PoAstV, PoSaV, PoNoV, and PoRVA, enabling the successful diagnosis of these four diseases.
Keywords: multiplex RT-qPCR; porcine astrovirus; porcine norovirus; porcine rotavirus species A; porcine sapovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment and application of a quadruplex real-time RT-qPCR assay for differentiation of TGEV, PEDV, PDCoV, and PoRVA.Microb Pathog. 2024 Jun;191:106646. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106646. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38631414
-
The development of a multiplex real-time RT-PCR for the detection of adenovirus, astrovirus, rotavirus and sapovirus from stool samples.J Virol Methods. 2017 Apr;242:30-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.12.016. Epub 2016 Dec 28. J Virol Methods. 2017. PMID: 28040514 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity of porcine enteric caliciviruses in pigs raised in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil.Arch Virol. 2010 Aug;155(8):1301-5. doi: 10.1007/s00705-010-0695-z. Epub 2010 Jun 6. Arch Virol. 2010. PMID: 20526786
-
[Diagnostic tests: Norovirus].Nihon Rinsho. 2005 Jul;63 Suppl 7:332-5. Nihon Rinsho. 2005. PMID: 16111266 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Global prevalence of Porcine Astrovirus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Prev Vet Med. 2025 May;238:106465. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2025.106465. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Prev Vet Med. 2025. PMID: 39954603
Cited by
-
A Quadruplex RT-qPCR for the Detection of Porcine Sapelovirus, Porcine Kobuvirus, Porcine Teschovirus, and Porcine Enterovirus G.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;15(7):1008. doi: 10.3390/ani15071008. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218401 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

