Characterization and Genomics of Pectinolytic Bacteria Isolated from Soft Rot Symptomatic Produce
- PMID: 39770355
- PMCID: PMC11728799
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13121096
Characterization and Genomics of Pectinolytic Bacteria Isolated from Soft Rot Symptomatic Produce
Abstract
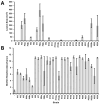
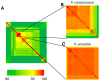
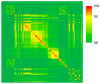
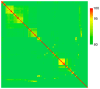
Bacterial soft rot causes major crop losses annually and can be caused by several species from multiple genera. These bacteria have a broad host range and often infect produce through contact with soil. The main genera causing bacterial soft rot are Pectobacterium and Dickeya, both of which have widespread geographical distribution. Because of many recent renaming and reclassifications of bacteria causing soft rot, identification and characterization of the causative agents can be challenging. In this work, we surveyed commercially available produce exhibiting typical soft rot symptoms, isolating pectinolytic bacteria and characterizing them genetically and phenotypically. We found that in our sampling, many samples were from the genus Pectobacterium; however, other genera were also capable of eliciting symptoms in potatoes, including an isolate from the genus Chryseobacterium. Genomic analyses revealed that many of the Pectobacterium isolates collected share prophages not found in other soft rot species, suggesting a potential role for these prophages in the evolution or fitness of these isolates. Our Chryseobacterium isolate was most similar to C. scophthalmum, a fish pathogen, suggesting that this isolate may be a crossover pathogen.
Keywords: Chryseobacterium; Pectobacterium; Pseudomonas; pectinolytic; soft rot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Charkowski A., Sharma K., Parker M.L., Secor G.A., Elphinstone J. Bacterial diseases of potato. In: Campos H., Ortiz O., editors. The Potato Crop: Its Agricultural, Nutritional and Social Contribution to Humankind. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. pp. 351–388.
-
- Kamau J.W., Ngaira J., Kinyua J., Gachamba S., Ngundo G., Janse J., Macharia I. Occurence of pectinolytic bacteria causing blackleg and soft rot of potato in Kenya. J. Plant Pathol. 2019;101:689–694. doi: 10.1007/s42161-018-00219-w. - DOI
-
- Czajkowski R., Perombelon M., Jafra S., Lojkowska E., Potrykus M., van der Wolf J., Sledz W. Detection, identification and differentiation of Pectobacterium and Dickeya species causing potato blackleg and tuber soft rot: A review. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2015;166:18–38. doi: 10.1111/aab.12166. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pinhero R.G., Coffin R., Yada R.Y. Advances in Potato Chemistry and Technology. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2009. Post-harvest storage of potatoes; pp. 339–370.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

