Targeting HBV cccDNA Levels: Key to Achieving Complete Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 39770359
- PMCID: PMC11728772
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13121100
Targeting HBV cccDNA Levels: Key to Achieving Complete Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
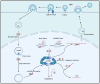
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) caused by HBV infection has brought suffering to numerous people. Due to the stable existence of HBV cccDNA, the original template for HBV replication, chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is difficult to cure completely. Despite current antiviral strategies being able to effectively limit the progression of CHB, complete CHB cure requires directly targeting HBV cccDNA. In this review, we discuss strategies that may achieve a complete cure of CHB, including inhibition of cccDNA de novo synthesis, targeting cccDNA degradation through host factors and small molecules, CRISP-Cas9-based cccDNA editing, and silencing cccDNA epigenetically.
Keywords: CRISP-cas9; HBV; cccDNA; chronic hepatitis B; interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Current Status and Challenges in Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Agents Based on Inactivation/Inhibition or Elimination of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA.Viruses. 2023 Nov 25;15(12):2315. doi: 10.3390/v15122315. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral strategies to eliminate hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA).Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;30:144-150. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2016.08.015. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27639371 Review.
-
HBV cccDNA: The Molecular Reservoir of Hepatitis B Persistence and Challenges to Achieve Viral Eradication.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 4;15(1):62. doi: 10.3390/biom15010062. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 39858456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive value of intrahepatic hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA and total DNA in patients with acute hepatitis B and patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving anti‑viral treatment.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Apr;9(4):1135-41. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.1972. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24566465
-
Metabolism and function of hepatitis B virus cccDNA: Implications for the development of cccDNA-targeting antiviral therapeutics.Antiviral Res. 2015 Oct;122:91-100. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.08.005. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 26272257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Intrinsically Disordered Region of HBx and Virus-Host Interactions: Uncovering New Therapeutic Approaches for HBV and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 10;26(8):3552. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083552. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reevaluating antiviral thresholds in HBV DNA-negative inactive HBsAg carriers: a multicenter histopathological analysis.Virol J. 2025 Jul 10;22(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02853-0. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40640910 Free PMC article.
-
The role of pioneering transcription factors, chromatin accessibility and epigenetic reprogramming in oncogenic viruses.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 16;16:1602497. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1602497. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40589575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Benefits of In Silico Methods: A Promising Alternative in Natural Compound's Drug Discovery and Repurposing for HBV Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 16;18(3):419. doi: 10.3390/ph18030419. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

