Does Combined Treatment with Tranexamic Acid and Vancomycin Affect Human Chondrocytes In Vitro?
- PMID: 39770418
- PMCID: PMC11677089
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121576
Does Combined Treatment with Tranexamic Acid and Vancomycin Affect Human Chondrocytes In Vitro?
Abstract
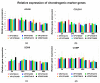
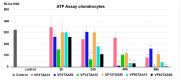
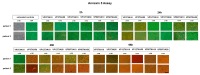
Background: The aim of our study was to examine the combined effects of tranexamic acid (TXA) and vancomycin powder (VP) on chondrocytes in vitro. Despite the use of TXA and VP being linked to a reduced risk of extensive postoperative blood loss and periprosthetic joint infections (PJIs) in TKA, the possible cytotoxic side effects on periarticular cell types remain unclear. Methods: Human chondrocytes were harvested from hyaline cartilage and expanded in monolayer culture before being simultaneously exposed to different concentrations of TXA and VP for varying exposure times. Cell viability and proliferation were assessed using an ATP assay and an Annexin 5 assay, respectively, while changes in the relative expression of chondrogenic marker genes were examined using semiquantitative RT-PCR. Results: The simultaneous exposure of chondrocytes to TXA and VP for more than 48 h led to a reduction in both cell viability and proliferation rates. When exposing chondrocytes to the lowest examined concentrations of both TXA (10 mg/mL) and VP (3 mg/mL), the observed effects were delayed until 96 h. However, our study found no dependencies of the observed effects on the concentrations tested. Further, we found no effects on the expression of chondrogenic marker genes. Conclusions: Consequently, limiting the exposure time of chondrocytes to TXA and VP in an in vitro setting to 24 h may be considered safe and could help to further improve the understanding of the safe use of substances in vivo. However, further in vitro research is required to develop a comprehensive understanding of the effects of both VP and TXA on important periarticular cell types in TKA, including chondrocytes, osteocytes, and tenocytes.
Keywords: chondrocytes; osteoarthritis; total joint replacement; toxicity; tranexamic acid; vancomycin powder; viability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Tranexamic Acid on Chondrocytes and Osteogenically Differentiated Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (hMSCs) In Vitro.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 29;9(12):3880. doi: 10.3390/jcm9123880. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33260331 Free PMC article.
-
Short exposure to tranexamic acid does not affect, in vitro, the viability of human chondrocytes.Eur J Med Res. 2019 Feb 22;24(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40001-019-0373-x. Eur J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 30795796 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Tranexamic Acid Cytotoxicity on In Vitro Chondrocytes.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015 Dec;44(12):E497-502. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015. PMID: 26665251
-
Toxicity of tranexamic acid (TXA) to intra-articular tissue in orthopaedic surgery: a scoping review.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 Jun;29(6):1862-1871. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06219-7. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 32860523
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing intrawound vancomycin powder and povidone iodine lavage in the prevention of periprosthetic joint infection of hip and knee arthroplasties.J Orthop Sci. 2024 Jan;29(1):165-176. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2022.11.013. Epub 2022 Dec 2. J Orthop Sci. 2024. PMID: 36470703
References
-
- Health at a Glance 2019 OECD Indicators: OECD Indicators. OECD Publishing; Paris, France: 2019.
-
- Jonsson H., Olafsdottir S., Sigurdardottir S., Aspelund T., Eiriksdottir G., Sigurdsson S., Harris T.B., Launer L., Gudnason V. Incidence and prevalence of total joint replacements due to osteoarthritis in the elderly: Risk factors and factors associated with late life prevalence in the AGES-Reykjavik Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016;17:14. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-0864-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klug A., Gramlich Y., Rudert M., Drees P., Hoffmann R., Weißenberger M., Kutzner K.P. The projected volume of primary and revision total knee arthroplasty will place an immense burden on future health care systems over the next 30 years. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2020;29:3287–3298. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06154-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

