Berbamine Promotes the Repair of Lower Limb Muscle Damage in Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia by Inhibiting Local Inflammation and NF-κB Nuclear Translocation
- PMID: 39770425
- PMCID: PMC11679954
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121583
Berbamine Promotes the Repair of Lower Limb Muscle Damage in Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia by Inhibiting Local Inflammation and NF-κB Nuclear Translocation
Abstract
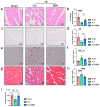
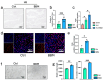
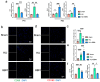
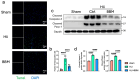
Background/Objectives: Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia (CLTI) is a chronic limb ischemic disease caused by vascular lesions, characterized by pain, ulcers, and gangrene, which can be life-threatening in severe cases. The objective of this study is to explore whether Berbamine (BBM) can protect against and repair ischemic muscle tissue in the lower limbs; Methods: Using a mouse hindlimb ischemia (HLI) model, 36 C57BL6 mice were divided into sham, HLI, and HLI+BBM treatment groups. Results: Our findings indicate that BBM can restore motor function and muscle tissue pathology in mice, potentially by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB), thereby alleviating tissue inflammation caused by chronic ischemia, reducing muscle cell apoptosis, inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization, and promoting angiogenesis. Conclusions: Our research suggests that BBM has the potential to protect against ischemic damage in lower limb muscle tissue, providing a new approach to the treatment of CLTI.
Keywords: apoptosis; berbamine; inflammation; limb ischemia; nuclear factor kappa-B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Conte M.S., Bradbury A.W., Kolh P., White J.V., Dick F., Fitridge R., Mills J.L., Ricco J.B., Suresh K.R., Murad M.H., et al. Global Vascular Guidelines on the Management of Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019;58:S1–S109.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.05.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Furubeppu H., Ito T., Kakuuchi M., Yasuda T., Kamikokuryo C., Yamada S., Maruyama I., Kakihana Y. Differential Regulation of Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Release in a Mouse Model of Skeletal Muscle Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front. Immunol. 2021;12:628822. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.628822. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

