Inhibition of the Biofilm Formation of Plant Streptococcus mutans
- PMID: 39770454
- PMCID: PMC11677685
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121613
Inhibition of the Biofilm Formation of Plant Streptococcus mutans
Abstract
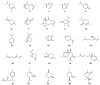
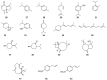
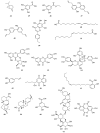
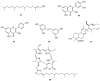
This review is devoted to a systematic analysis of studies aimed at investigating plant extracts, essential oils and phytochemical compounds capable of inhibiting Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation. This paper investigates the effect of extracts, essential oils and individual plant compounds on inhibiting the biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans, one of the major pathogens responsible for the development of dental caries. Using cultural microbiology and molecular biology techniques, the authors describe the mechanisms by which plant samples reduce Streptococcus mutans adhesion and growth. The results show that several plant components have antibacterial properties, contributing to the reduction of Streptococcus mutans colony numbers and inhibiting the synthesis of extract-exopolysaccharide matrices required for biofilm formation. This work highlights the potential of botanicals in inhibiting Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation, which can be applied as natural antimicrobial agents in the prevention and treatment of dental diseases. Views on the use of these plant extracts and their components in dental preparations such as toothpastes, rinses and gels aimed at preventing dental caries are evaluated. The review shows the relevance of the research to optimizing the use of plant extracts, essential oils, individual compounds and their active actions in the control of Streptococcus mutans biofilms.
Keywords: Streptococcus mutans; biofilm formation; dental caries; microbial ecology; plants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of anti-biofilm and anti- adherence potential of plant extracts against Streptococcus mutans: A therapeutic approach for oral health.Microb Pathog. 2024 Mar;188:106514. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106514. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38296118
-
Effects of Antimicrobial Peptide GH12 on the Cariogenic Properties and Composition of a Cariogenic Multispecies Biofilm.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Nov 30;84(24):e01423-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01423-18. Print 2018 Dec 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30341079 Free PMC article.
-
Six Spain Thymus essential oils composition analysis and their in vitro and in silico study against Streptococcus mutans.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Apr 5;23(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03928-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37020229 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation by strategies targeting the metabolism of exopolysaccharides.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2021 Sep;47(5):667-677. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2021.1915959. Epub 2021 May 3. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33938347 Review.
-
Antibacterial effects of natural compounds on biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2022 Dec;8(6):1426-1433. doi: 10.1002/cre2.673. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2022. PMID: 36281582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grand View Research Pediatric Dental Market Report. [(accessed on 30 October 2024)]. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/pediatric-dental-mar....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

