Documentary Analysis of Hypericum perforatum (St. John's Wort) and Its Effect on Depressive Disorders
- PMID: 39770466
- PMCID: PMC11728764
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121625
Documentary Analysis of Hypericum perforatum (St. John's Wort) and Its Effect on Depressive Disorders
Abstract
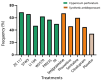
Hypericum perforatum, also known as St. John's Wort, pericon, or yellow grass, is known for its antidepressant potential. It could represent a natural alternative to current pharmacological antidepressant treatments, which have a high incidence of side effects in patients and therefore lead to early dropouts. Through a bibliographic revision of clinical trials and information collected from scientific articles during the first period of 2020, we aimed to evaluate whether its administration could be beneficial in the treatment of mild-to-moderate depression, with fewer side effects compared to synthetic drugs. Among the main components, hypericin and hyperforin have been related to the observed antidepressant activity; therefore, their possible mechanism of action was reviewed and highlighted. Furthermore, patients receiving Hypericum extracts were less likely to withdraw from studies because of adverse effects compared to those receiving older standard antidepressants. This review aims to provide suggestions for an alternative treatment of mild-to-moderate depression disorder under the supervision of a medical doctor, since, although it appears to be a potentially efficient treatment with a low presence of adverse effects in comparison to synthetic antidepressants, it might also interact with other medications and lead to therapeutic failures if misused for self-medication.
Keywords: antidepressants; medicinal plants; naphthodianthrones; phloroglucinols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx) [(accessed on 4 March 2023)]. Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/
-
- Depressive Disorder (Depression) [(accessed on 29 November 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC, USA: 2013. - DOI
-
- VizHub—GBD Results. [(accessed on 6 October 2024)]. Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

