Study of Interactions Between Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents and Collagen by Taylor Dispersion Analysis and Frontal Analysis Continuous Capillary Electrophoresis
- PMID: 39770475
- PMCID: PMC11728588
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121633
Study of Interactions Between Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents and Collagen by Taylor Dispersion Analysis and Frontal Analysis Continuous Capillary Electrophoresis
Abstract
Background: Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) are widely used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to enhance image contrast by interacting with water molecules, thus improving diagnostic capabilities. However, understanding the residual accumulation of GBCA in tissues after administration remains an area of active research. This highlights the need for advanced analytical techniques capable of investigating interactions between GBCAs and biopolymers, such as type I collagen, which are abundant in the body.
Objective: This study explores the interactions of neutral and charged GBCAs with type I collagen under physiological pH conditions (pH 7.4) using Taylor dispersion analysis (TDA) and frontal analysis continuous capillary electrophoresis (FACCE).
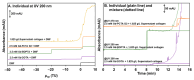
Methods: Collagen from bovine achilles tendon was ground using a vibratory ball mill to achieve a more uniform particle size and increased surface area. Laser granulometry was employed to characterize the size distributions of both raw and ground collagen suspensions in water. TDA was used to assess the hydrodynamic radius (Rh) of the soluble collagen fraction present in the supernatant.
Results: From the TDA and FACCE results, it was shown that there were no significant interactions between the tested GBCAs and either the ground collagen or its soluble fraction at pH 7.4. Interestingly, we also observed that collagen interacts with filtration membranes, indicating that careful selection of membrane material, or the absence of filtration in the experimental protocol, is essential in interaction studies involving collagen.
Conclusion: These findings bring valuable insights into the behavior of GBCAs in biological systems with potential implications for clinical applications.
Keywords: Taylor dispersion analysis; collagen; frontal analysis continuous capillary electrophoresis; gadolinium-based contrast agents; interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Lacampagne A., Gannier F., Argibay J., Garnier D., Guennec J.-Y.L. The stretch-activated ion channel blocker gadolinium also blocks L-type calcium channels in isolated ventricular myocytes of the guinea-pig. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1994;1191:205–208. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90250-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lauffer R.B. Paramagnetic metal complexes as water proton relaxation agents for NMR imaging: Theory and design. Chem. Rev. 1987;87:901–927. doi: 10.1021/cr00081a003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

