Scientific Validation of Using Active Constituent as Research Focus in Traditional Chinese Medicine: Case Study of Pueraria lobata Intervention in Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 39770517
- PMCID: PMC11678734
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121675
Scientific Validation of Using Active Constituent as Research Focus in Traditional Chinese Medicine: Case Study of Pueraria lobata Intervention in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
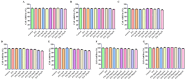
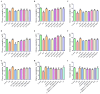
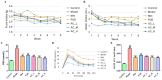
Objectives: Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is recognized for its complex composition and multiple therapeutic targets. However, current pharmacological research often concentrates on extracts or individual components. The former approach faces numerous challenges, whereas the latter oversimplifies and disregards the synergistic effects among TCM components. This study aims to investigate the scientific validity of focusing on the active constituent in TCM efficacy research, using Pueraria lobata (P. lobata) as a case study. Methods: Through spectrum-effect correlation analysis, network pharmacology, and molecular docking, five active ingredients of P. lobata were identified: puerarin, formononetin, tuberosin, 4',7-dihdroxy-3'-methoxyisoflavone, and Daidzein-4,7-diglucoside. These ingredients were combined to form an active constituent, which was subsequently tested in vitro and in vivo. Results: In in vitro, the active constituent exhibited superior effects in enhancing glucose consumption and glycogen synthesis compared to both the P. lobata extract and individual components. In vivo experiments demonstrated that medium and high doses of the active constituent were significantly more effective than P. lobata extract, with effects comparable to those of metformin in reducing blood sugar levels. Conclusions: The active constituent effectively improves T2DM by lowering blood glucose levels, promoting glycogen synthesis, and modulating glycolipid metabolism. Both in vitro and in vivo studies indicate that it outperformed the P. lobata extract and individual components. This study establishes the scientific validity and feasibility of utilizing the active constituent as the focus for investigating the efficacy of TCM, thereby offering novel insights and a new research paradigm for future TCM investigations.
Keywords: Pueraria lobata; active constituent; potential pharmacodynamic ingredients; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Lee S.-H., Min K.-H., Han J.-S., Lee D.-H., Park D.-B., Jung W.-K., Park P.-J., Jeon B.-T., Kim S.-K., Jeon Y.-J. Effects of Brown Alga, Ecklonia Cava on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/KsJ-Db/Db Mice, a Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012;50:575–582. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.12.032. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

