Effect of Mn(II) and Co(II) on Anti- Candida Metabolite Production by Aspergillus sp. an Endophyte Isolated from Dizygostemon riparius (Plantaginaceae)
- PMID: 39770520
- PMCID: PMC11677262
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121678
Effect of Mn(II) and Co(II) on Anti- Candida Metabolite Production by Aspergillus sp. an Endophyte Isolated from Dizygostemon riparius (Plantaginaceae)
Abstract
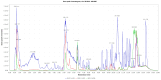
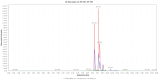
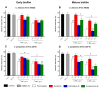
Background/Objectives: This study evaluates the effect of Mn(II) and Co(II) ions on the production of anti-Candida metabolites by the endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp., isolated from Dizygostemon riparius. The objective was to identify metal-induced secondary metabolites with antifungal potential against drug-resistant Candida species. Methods: Aspergillus sp. was cultivated in Czapek agar supplemented with MnCl₂ (400 µM) or CoCl₂ (200 µM). Metabolite profiles were analyzed using UHPLC-DAD and LC-ESI-HRMS, followed by structural elucidation via NMR. Antifungal and biofilm inhibition activities were tested against Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis. Toxicity was assessed using Tenebrio molitor larvae. Results: Key metabolites, including pyrophen, penicillquei B, and fonsecinone B, demonstrated antifungal activity with MIC values of 4.37-280.61 µg/mL. Fonsecinone B exhibited superior biofilm inhibition, surpassing fluconazole in reducing biofilm biomass and viability. In vivo assays showed low toxicity, with survival rates above 80% at 2× MIC/kg. Conclusions: Mn(II) and Co(II) significantly modulated the production of antifungal metabolites in Aspergillus sp. Fonsecinone B emerged as a promising candidate for antifungal therapy due to its potent activity and low toxicity. These findings support further investigation into the therapeutic potential of metal-induced fungal metabolites for combating drug-resistant Candida infections.
Keywords: anti-Candida metabolites; endophytic fungi; metal-induced secondary metabolism; natural products biotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures











References
-
- Tkaczuk C., Majchrowska-Safaryan A., Panasiuk T., Tipping C. Effect of selected heavy metal ions on the growth of entomopathogenic fungi from the genus Isaria. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019;17:2571–2582. doi: 10.15666/aeer/1702_25712582. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

