The Application of the Design of Experiments and Artificial Neural Networks in the Development of a Fast and Straightforward HPLC-UV Method for Fluconazole Determination in Hemato-Oncologic Pediatric Patients and Its Adaptation to Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
- PMID: 39770521
- PMCID: PMC11679493
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121679
The Application of the Design of Experiments and Artificial Neural Networks in the Development of a Fast and Straightforward HPLC-UV Method for Fluconazole Determination in Hemato-Oncologic Pediatric Patients and Its Adaptation to Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Abstract
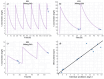
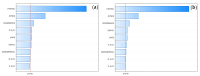
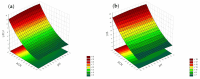
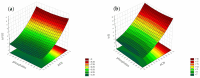
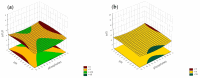
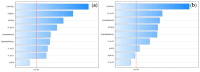
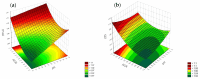
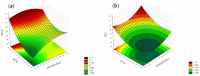
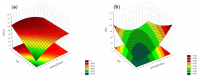
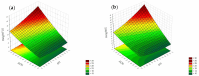
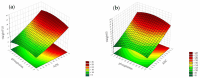
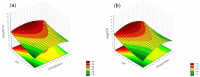
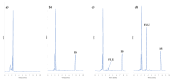
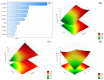
Objectives: This study aimed to develop an optimized and wide concentration range HPLC-UV method for fluconazole (FLU) determination and its adaptation for pharmacokinetics (PK) studies in the pediatric population. Methods: The following parameters of chromatographic separation were optimized: retention time, tailing factor, peak height, and the sample preconditioning parameter, such as recovery. The optimization process involved the use of a central composite design (CCD) and Box-Behnken design (BBD) in the design of experiments (DoE) approach and a multilayer perceptron (MLP) for artificial neural network (ANN) application. Statistical and PK analyses were performed using Statistica and PKanalix. Results: The acetonitrile (ACN) concentration revealed the most significant factor influencing the retention time, tailing factor, and peak height of FLU and the internal standard. For recovery, the extracting agent's volume was the most significant factor. In most cases, the analysis conducted with the DoE and ANN indicated the same factors in a similar order regarding their impact on the analyzed variables. The optimization process allowed for achieving a wide range of determined concentrations (0.5-100 mg/L) and ~100% recovery. The developed method enabled PK analysis of 12 samples from three pediatric patients, proving its clinical usability. The estimated median clearance (CL) and volume of distribution (Vd) were 1.01 L/h and 18.64 L, respectively. Conclusions: DoE and ANNs are promising and useful tools in the optimization of sample preconditioning as well as the HPLC separation procedure. The investigated fluconazole determination method meets the European Medicines Agency (EMA) validation objectives and might be used in pediatric and adult PK studies.
Keywords: Box–Behnken design; HPLC-UV; central composite design; human plasma; machine learning; method optimization; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Machine Learning-Enabled NIR Spectroscopy. Part 3: Hyperparameter by Design (HyD) Based ANN-MLP Optimization, Model Generalizability, and Model Transferability.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Dec 7;24(8):254. doi: 10.1208/s12249-023-02697-3. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 38062329
-
The application of Box-Behnken-Design in the optimization of HPLC separation of fluoroquinolones.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 19;9(1):19458. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55761-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31857613 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Design of Experiments® Approach-Driven Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Systematic Optimization of Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography Method to Analyze Simultaneously Two Drugs (Cyclosporin A and Etodolac) in Solution, Human Plasma, Nanocapsules, and Emulsions.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 May 13;22(4):155. doi: 10.1208/s12249-021-02026-6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 33987739
-
Design of experiments and artificial neural networks as useful tools in the optimization of analytical procedure.Polim Med. 2024 Jul-Dec;54(2):113-116. doi: 10.17219/pim/196209. Polim Med. 2024. PMID: 39610258 Review.
-
Machine Learning-Enabled NIR Spectroscopy. Part 2: Workflow for Selecting a Subset of Samples from Publicly Accessible Data.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Jan 10;24(1):34. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02493-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 36627410 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Pharmaceutical Analytical Technology.Molecules. 2025 May 14;30(10):2155. doi: 10.3390/molecules30102155. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40430327 Free PMC article.
-
Fluconazole Dosing for the Prevention of Candida spp. Infections in Hemato-Oncologic Pediatric Patients: Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Probability of Target Attainment Simulations.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 8;17(4):488. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040488. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diflucan—Referral|European Medicines Agency (EMA) [(accessed on 4 October 2024)]. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/referrals/diflucan.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

