The Possible Role of Plant-Based Bars Consumption in CKD Geriatric Patients
- PMID: 39770530
- PMCID: PMC11677204
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121689
The Possible Role of Plant-Based Bars Consumption in CKD Geriatric Patients
Abstract
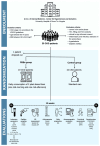
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) geriatric patients experience a premature aging process, compared with the general population of the same age and sex. The uremic milieu is capable of enhancing oxidative stress (OS) and microinflammation, leading to a pro-aging mechanism and an increased protein catabolism. Moreover, cognitive disorders are observed. Objectives: The aim of this pilot study was to evaluate the possible beneficial effects on the body composition, cognitive functions, inflammatory state and OS of CKD-geriatric patients induced by the consumption of two different plant-based bars (PBBs). Methods: A total of 20 male (mean age 73 ± 7 years) and 9 female patients (mean age 71 ± 4 years) were enrolled, divided as follows: 19 in the PBBs group (that consumed both bars) and 10 in the control group. They were monitored for 12 weeks. The PBBs presented a moderate caloric value and were enriched with waste and by-products of wine and olive oil supply chains and with organic saffron. Results and Conclusions: At the end of this study, the PBBs group, compared to the control group, showed an improvement in their body composition, detected by bioimpedance analysis and ultrasound examination, and in their cognitive function, revealed by mini-mental state examination. In the PBBs group, we also observed an OS reduction, through the free oxygen radical test.
Keywords: Crocus sativus L.; Olea europaea L.; Vitis vinifera L.; antioxidants; chronic kidney disease; depressive disorders; elderly; polyphenols; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Piccoli G.B., Cederholm T., Avesani C.M., Bakker S.J.L., Bellizzi V., Cuerda C., Cupisti A., Sabatino A., Schneider S., Torreggiani M., et al. Nutritional status and the risk of malnutrition in older adults with chronic kidney disease—Implications for low protein intake and nutritional care: A critical review endorsed by ERN-ERA and ESPEN. Clin. Nutr. 2023;42:443–457. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.01.018. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

