Osteoporosis: Causes, Mechanisms, Treatment and Prevention: Role of Dietary Compounds
- PMID: 39770539
- PMCID: PMC11679375
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121697
Osteoporosis: Causes, Mechanisms, Treatment and Prevention: Role of Dietary Compounds
Abstract
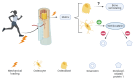
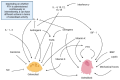
Osteoporosis is a chronic disease that is characterized by a loss of bone density, which mainly affects the microstructure of the bones due to a decrease in bone mass, thereby making them more fragile and susceptible to fractures. Osteoporosis is currently considered one of the pandemics of the 21st century, affecting around 200 million people. Its most serious consequence is an increased risk of bone fractures, thus making osteoporosis a major cause of disability and even premature death in the elderly. In this review, we discuss its causes, the biochemical mechanisms of bone regeneration, risk factors, pharmacological treatments, prevention and the effects of diet, focusing in this case on compounds present in a diet that could have palliative and preventive effects and could be used as concomitant treatments to drugs, which are and should always be the first option. It should be noted as a concluding remark that non-pharmacological treatments such as diet and exercise have, or should have, a relevant role in supporting pharmacology, which is the recommended prescription today, but we cannot ignore that they can have a great relevance in the treatment of this disease.
Keywords: bone regeneration; diet; disease prevention; lifestyle; nutraceuticals; osteoporosis; oxidative stress; pharmacological treatments; polyphenols; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Salari N., Ghasemi H., Mohammadi L., Behzadi M.H., Rabieenia E., Shohaimi S., Mohammadi M. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. [(accessed on 22 April 2024)];J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021 16:609. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02772-0. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8522202/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

