Salidroside: An Overview of Its Promising Potential and Diverse Applications
- PMID: 39770545
- PMCID: PMC11678419
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121703
Salidroside: An Overview of Its Promising Potential and Diverse Applications
Abstract
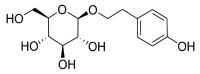
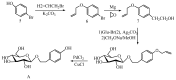
Salidroside, a phenolic compound isolated from various Rhodiola plants, is the principal active constituent of Traditional Chinese Medicine known for its adaptogenic properties. Due to the challenging environment of Rhodiola species, such as high altitude, high radiation, drought, and hypoxia, the source of salidroside is scarce. However, numerous studies have shown that salidroside has a range of biological activities, including cardiovascular and central nervous system activity, and anti-hypoxia, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging activities. Although previous studies have partially summarized the pharmacological effects of salidroside, the overall pharmacological effects have not been analyzed. Hence, this review will systematically summarize the isolation, purification, synthesis, derivatization, pharmacological activity, pharmacokinetics, clinical application, and safety of salidroside. It is expected to provide new insights for the further research and pharmaceutical development of salidroside.
Keywords: clinical application; pharmacology; review; safety; salidroside; signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



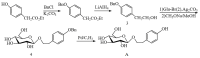












References
-
- Zheng L., Wang Z., Zhang B., Yan L., Wang P., Zhao C., Wang J., Wang Y., Lin H., Qiu L., et al. Rhodiola rosea L. improved intestinal digestive enzyme activities, inflammatory response, barrier, and microbiota dysbiosis in Lateolabrax maculatus juveniles fed with high-carbohydrate diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024;146:109362. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109362. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

