Mass Spectrometric Based Metabolomics of the Saudi Cultivar of Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.): A Combined GC-MS, Antimicrobial and Computational Approach
- PMID: 39770575
- PMCID: PMC11677947
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17121733
Mass Spectrometric Based Metabolomics of the Saudi Cultivar of Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.): A Combined GC-MS, Antimicrobial and Computational Approach
Abstract
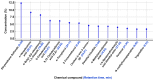
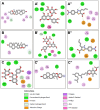
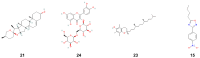
Background and Objective: In Saudi Arabia, numerous plant species with promising medicinal properties are cultivated, widely traded, and commonly utilized in traditional medicine, including fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum). This study aimed to comprehensively assess the phytochemical composition and antimicrobial potential of the Saudi cultivar of fenugreek using an integrative approach combining in vitro and in silico methodologies. Methods: A comprehensive investigation was conducted on the ethanol extract of fenugreek seeds, assessing its antibacterial, antifungal, properties. Computational modeling was employed to predict pharmacokinetic behavior and potential toxicity of the identified bioactive compounds. Results: Qalitative phytochemical analysis showed presence of alkaloids, tannins, saponins, glycosides, flavonoids, and steroids, while terpenoids were notably absent. GC-MS analysis of Trigonella foenum-graecum (fenugreek) seeds identified 25 bioactive compounds, with Ethyl methane sulfonate (12.41%) being the predominant component. Other key compounds included n-Hexadecanoic acid, 4-Butyl-2(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole, and α-Tocopherol. In silico modeling of fenugreek phytochemicals supported their antibacterial, antioxidant, and neuroprotective potential, with compounds 21 and 24 showing strong binding to key targets like Tyrosyl-tRNA Synthetase (TyrRS) of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Aspartic proteinase from Candida albicans (C. albicans) and human peroxiredoxin 5. Pharmacokinetic analysis indicated good oral bioavailability, minimal CYP inhibition, and blood-brain barrier penetration, suggesting potential for treating neurodegenerative diseases. These bioactive compounds, including diosgenin and trigonelline, support fenugreek's therapeutic promise and warrant further in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies. Conclusion: The Saudi fenugreek cultivar is rich in bioactive compounds with good antibacterial potential. These findings establish a robust foundation for continued pharmacological research on the Saudi cultivar of T. foenum-graecum, highlighting its potential as a rich source of bioactive compounds with significant medicinal value.
Keywords: anti-bacterial agents; chemical composition; computational biology; fenugreek; fungi; in vitro study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdallah E.M. Plants: An alternative source for antimicrobials. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011;1:16–20.
-
- Hoareau L., DaSilva E.J. Medicinal plants: A re-emerging health aid. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 1999;2:3–4.
-
- Yusupova Z., Baratjon Ogli S.F., Abduqunduzovna M.Z. Medicinal plants growing in our republic medicinal properties. Period. J. Mod. Philos. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2023;15:5–7.
-
- Giannenas I., Sidiropoulou E., Bonos E., Christaki E., Florou-Paneri P. Feed Additives. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. The history of herbs, medicinal and aromatic plants, and their extracts: Past, current situation and future perspectives; pp. 1–18.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

