Salmonella Phage vB_SpuM_X5: A Novel Approach to Reducing Salmonella Biofilms with Implications for Food Safety
- PMID: 39770603
- PMCID: PMC11678034
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12122400
Salmonella Phage vB_SpuM_X5: A Novel Approach to Reducing Salmonella Biofilms with Implications for Food Safety
Abstract
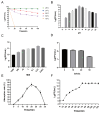
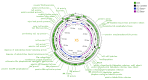
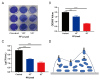
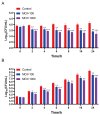
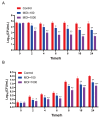
Salmonella, a prevalent foodborne pathogen, poses a significant social and economic strain on both food safety and public health. The application of phages in the control of foodborne pathogens represents an emerging research area. In this study, Salmonella pullorum phage vB_SpuM_X5 (phage X5) was isolated from chicken farm sewage samples. The results revealed that phage X5 is a novel Myoviridae phage. Phage X5 has adequate temperature tolerance (28 °C-60 °C), pH stability (4-12), and a broad host range of Salmonella bacteria (87.50% of tested strains). The addition of phage X5 (MOI of 100 and 1000) to milk inoculated with Salmonella reduced the number of Salmonella by 0.72 to 0.93 log10 CFU/mL and 0.66 to 1.06 log10 CFU/mL at 4 °C and 25 °C, respectively. The addition of phage X5 (MOI of 100 and 1000) to chicken breast inoculated with Salmonella reduced bacterial numbers by 1.13 to 2.42 log10 CFU/mL and 0.81 to 1.25 log10 CFU/mL at 4 °C and 25 °C, respectively. Phage X5 has bactericidal activity against Salmonella and can be used as a potential biological bacteriostatic agent to remove mature biofilms of Salmonella or for the prevention and control of Salmonella.
Keywords: Salmonella; bacteriostatic agent; biofilm; phage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bio-Control of Salmonella Enteritidis in Foods Using Bacteriophages.Viruses. 2015 Aug 24;7(8):4836-53. doi: 10.3390/v7082847. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26305252 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a Broad Range Lytic Phage LPST94 for Biological Control of Salmonella in Foods.Microorganisms. 2020 Feb 13;8(2):247. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8020247. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32069865 Free PMC article.
-
Morphologic and genomic characterization of a broad host range Salmonella enterica serovar Pullorum lytic phage vB_SPuM_SP116.Microb Pathog. 2019 Nov;136:103659. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103659. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31398528
-
A Polyvalent Broad-Spectrum Escherichia Phage Tequatrovirus EP01 Capable of Controlling Salmonella and Escherichia coli Contamination in Foods.Viruses. 2022 Jan 29;14(2):286. doi: 10.3390/v14020286. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215879 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and genomic analysis of Salmonella Abortusequi phage, vB_SalP_LDDK01, and its biocontrol application in donkey meat.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Dec 23;14:1527201. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1527201. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39764155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007–2015. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2015.
-
- Li K., Ye S., Alali W.Q., Wang Y., Wang X., Xia X., Yang B. Antimicrobial susceptibility, virulence gene and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium recovered from retail raw chickens, China. Food Control. 2017;72:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.07.032. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2662024FW012/Rural revitalization science and technology of Jingchuxing program, Huazhong Agricultural University
- 2022YFD1800602/State Key Research and development program
- CARS-41/the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA
- 2021CFA019/he Key Projects of Hubei Natural Science Foundation
- 2022BBA0055/and the Key Research and Development Project of Hubei Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

