Highly Targeted Detection of Priority Phytopathogen Pectobacterium brasiliense: From Obtaining Polyclonal Antibodies to Development and Approbation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Lateral Flow Immunoassay
- PMID: 39770641
- PMCID: PMC11676143
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12122436
Highly Targeted Detection of Priority Phytopathogen Pectobacterium brasiliense: From Obtaining Polyclonal Antibodies to Development and Approbation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Lateral Flow Immunoassay
Abstract
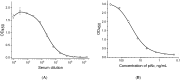
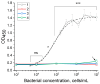
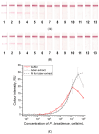
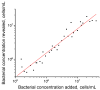
Pectobacterium brasiliense is a bacterial phytopathogen that causes soft and black rot and actively spreads worldwide. Our study is the first development of immunoassays for detecting P. brasiliense. We immunized rabbits and obtained serum with an extremely high titer (1:108). Isolated polyclonal antibodies were tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using 18 closely related strains and 5 non-related bacterial pathogens. No cross-reactivity was found concerning the tested pathogens. The ELISA of P. brasiliense was developed in a double-antibody sandwich format with a detection limit of 1.5 × 104 cells/mL. A lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) for P. brasiliense was also developed in a double-antibody sandwich format with a detection limit of 1 × 105 cells/mL. The results of P. brasiliense cells testing with LFIA in plant matrix showed a high correlation (R2 = 0.932) between concentrations of added and revealed cells. When testing potato seed material, ELISA and LFIA confirmed 75 and 66% of positive samples according to real-time PCR, respectively. For negative samples, ELISA showed 84% coincidence, and LFIA coincided with PCR for 89% of samples. Thus, the developed immunoassays can be used to evaluate plant material in poorly equipped conditions or under field testing.
Keywords: ELISA; Pectobacterium brasiliense; lateral flow immunoassay; phytopathogen; polyclonal antibodies; potato soft rot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sun Y., Utpal H., Wu Y., Sun Q., Feng Z., Shen Y., Zhang R., Zhou X., Wu J. Comparative genomic and transcriptome analyses of two Pectobacterium brasiliense strains revealed distinct virulence determinants and phenotypic features. Front. Microbiol. 2024;15:1362283. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1362283. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

